Page 56 -
P. 56
MEMS Fabrication 3-11
<100>
W m
z = Etch depth
54.74°
t = z Si <111>
si
W
o
Anisotropic etching of (100) silicon
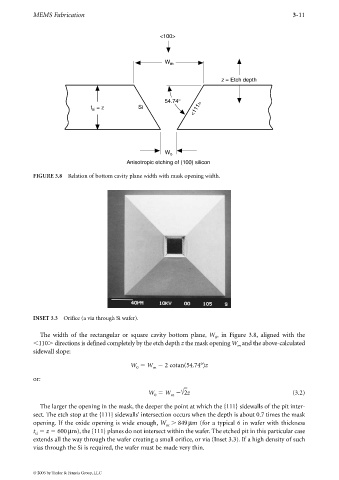
FIGURE 3.8 Relation of bottom cavity plane width with mask opening width.
INSET 3.3 Orifice (a via through Si wafer).
The width of the rectangular or square cavity bottom plane, W , in Figure 3.8, aligned with the
0
110 directions is defined completely by the etch depth z the mask opening W and the above-calculated
m
sidewall slope:
W W 2 cotan(54.74°)z
m
0
or:
W W 2 z (3.2)
0 m
The larger the opening in the mask, the deeper the point at which the {111} sidewalls of the pit inter-
sect. The etch stop at the {111} sidewalls’ intersection occurs when the depth is about 0.7 times the mask
opening. If the oxide opening is wide enough, W 849µm (for a typical 6 in wafer with thickness
m
t z 600µm), the {111} planes do not intersect within the wafer. The etched pit in this particular case
si
extends all the way through the wafer creating a small orifice, or via (Inset 3.3). If a high density of such
vias through the Si is required, the wafer must be made very thin.
© 2006 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC