Page 302 - Machine Learning for Subsurface Characterization
P. 302
264 Machine learning for subsurface characterization
4.1.2 Support vector machine (SVM) classifier
SVM was originally designed to create highly generalizable classifier for binary
classification. SVM transforms the original feature space into a higher-
dimensional space based ona user-defined kernel function and thenfinds support
vectors to maximize the separation (margin) between two classes. SVM first
approximates a hyperplane that separates both the classes. Accordingly, SVM
selects samples from both the classes, referred as support vectors, that are closest
to the hyperplane. The total separation between the hyperplane and the support
vectors is referred as margin. SVM then iteratively optimizes the hyperplane and
supports vectors to maximize the margin, thereby finding the most generalizable
decision boundaries. When the dataset is separable by nonlinear boundary, cer-
tain kernels are implemented in the SVM to appropriately transform the feature
space. For a dataset that is not easily separable, soft margin is used to avoid over-
fitting by giving less weightage to classification errors around the decision
boundaries. In this study, we use two SVM classifiers, one with linear kernel
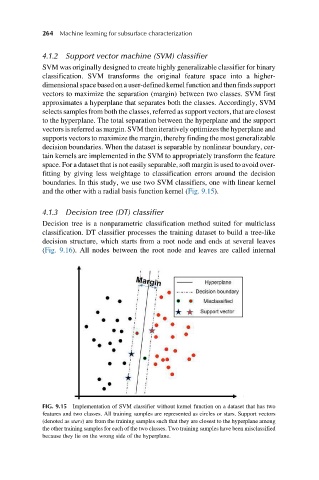
and the other with a radial basis function kernel (Fig. 9.15).
4.1.3 Decision tree (DT) classifier
Decision tree is a nonparametric classification method suited for multiclass
classification. DT classifier processes the training dataset to build a tree-like
decision structure, which starts from a root node and ends at several leaves
(Fig. 9.16). All nodes between the root node and leaves are called internal
FIG. 9.15 Implementation of SVM classifier without kernel function on a dataset that has two
features and two classes. All training samples are represented as circles or stars. Support vectors
(denoted as stars) are from the training samples such that they are closest to the hyperplane among
the other training samples for each of the two classes. Two training samples have been misclassified
because they lie on the wrong side of the hyperplane.