Page 301 - Machine Learning for Subsurface Characterization
P. 301
Classification of sonic wave Chapter 9 263
by using multipoint compressional wavefront travel-time measurements.
Hyperparameter optimization is performed using grid search along with five-
fold cross validation to ensure the generalization of the trained classifiers.
The classification models will facilitate the categorization of materials contain-
ing discontinuities of various spatial characteristics solely based on multipoint
measurements of compressional wavefront arrival times.
4.1.1 K-nearest neighbors (KNN) classifier
For a new, unseen, unlabeled sample, KNN selects K neighboring samples from
the training/testing dataset that are most similar to the new sample. Similarity
between two points is measured in terms of Minkowski distance between them
in the feature space. Following that, the new unlabeled sample is assigned a
class based on the majority class among the K neighboring samples selected
from the training/testing dataset. KNN does not require an explicit training
stage. KNN is a nonparametric model because the model does not require to
learn any parameter (e.g., weight or bias). Nonetheless, to ensure the general-
izability of KNN model, certain hyperparameters, such as K and distance met-
ric, need to be adjusted so as to obtain good performance on the testing dataset.
Increase in K leads to underfitting of the KNN model (high bias). When K is
low, the KNN model is easily affected by outliers, resulting in model overfitting
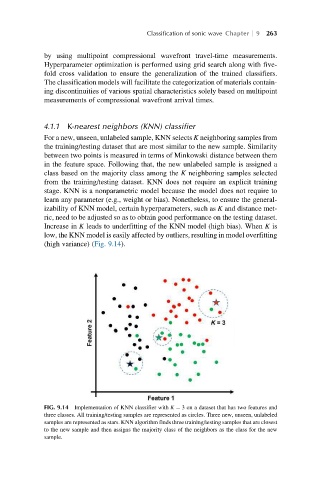
(high variance) (Fig. 9.14).
FIG. 9.14 Implementation of KNN classifier with K ¼ 3 on a dataset that has two features and
three classes. All training/testing samples are represented as circles. Three new, unseen, unlabeled
samples are represented as stars. KNN algorithm finds three training/testing samples that are closest
to the new sample and then assigns the majority class of the neighbors as the class for the new
sample.