Page 304 - Machine Learning for Subsurface Characterization
P. 304
266 Machine learning for subsurface characterization
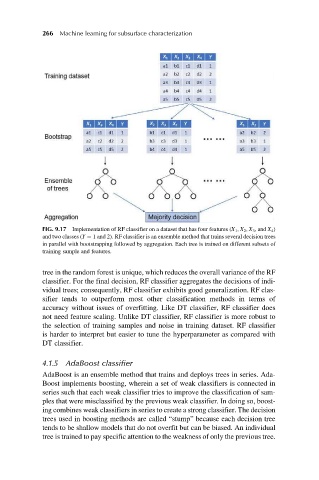
FIG. 9.17 Implementation of RF classifier on a dataset that has four features (X 1 , X 2 , X 3 , and X 4 )
and two classes (Y ¼ 1 and 2). RF classifier is an ensemble method that trains several decision trees
in parallel with bootstrapping followed by aggregation. Each tree is trained on different subsets of
training sample and features.
tree in the random forest is unique, which reduces the overall variance of the RF
classifier. For the final decision, RF classifier aggregates the decisions of indi-
vidual trees; consequently, RF classifier exhibits good generalization. RF clas-
sifier tends to outperform most other classification methods in terms of
accuracy without issues of overfitting. Like DT classifier, RF classifier does
not need feature scaling. Unlike DT classifier, RF classifier is more robust to
the selection of training samples and noise in training dataset. RF classifier
is harder to interpret but easier to tune the hyperparameter as compared with
DT classifier.
4.1.5 AdaBoost classifier
AdaBoost is an ensemble method that trains and deploys trees in series. Ada-
Boost implements boosting, wherein a set of weak classifiers is connected in
series such that each weak classifier tries to improve the classification of sam-
ples that were misclassified by the previous weak classifier. In doing so, boost-
ing combines weak classifiers in series to create a strong classifier. The decision
trees used in boosting methods are called “stump” because each decision tree
tends to be shallow models that do not overfit but can be biased. An individual
tree is trained to pay specific attention to the weakness of only the previous tree.