Page 308 - Machine Learning for Subsurface Characterization
P. 308
270 Machine learning for subsurface characterization
function, whereas the activation function of neurons in the output layer for a
regression task is usually a linear filter and for a classification task is usually
a softmax filter.
When a feature vector is fed to the input layer of ANN model, the input
values are propagated forward through the network, neuron by neuron and layer
by layer, until the sequence of mathematical transformations (weight, bias, and
activation function) applied on the feature vector reaches the output layer. Acti-
vation functions are added to each neuron to allow the ANN to account for non-
linear behavior in the training dataset. Stacking of the layers facilitates the
nonlinear capabilities of ANN for complex function approximation. The flex-
ibility of ANN leads to overfitting issues that can be handled through hyperpara-
meter tuning. ANN training involves feedforward of data signals to generate the
output and then the backpropagation of errors for gradient descent optimization.
During the process of training an ANN model, first, the weights/biases for the
neurons in the output layer are updated; then, the weights/biases of the neurons
of each preceding layer are iteratively updated, till the weights/biases of neu-
rons of the first hidden layer are updated.
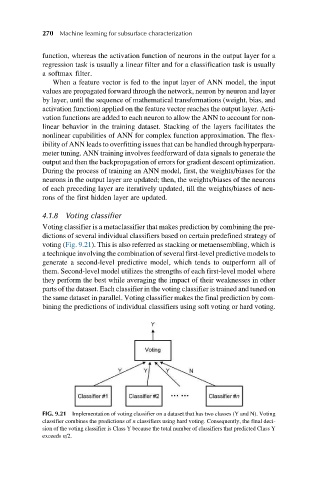
4.1.8 Voting classifier
Voting classifier is a metaclassifier that makes prediction by combining the pre-
dictions of several individual classifiers based on certain predefined strategy of
voting (Fig. 9.21). This is also referred as stacking or metaensembling, which is
a technique involving the combination of several first-level predictive models to
generate a second-level predictive model, which tends to outperform all of
them. Second-level model utilizes the strengths of each first-level model where
they perform the best while averaging the impact of their weaknesses in other
parts of the dataset. Each classifier in the voting classifier is trained and tuned on
the same dataset in parallel. Voting classifier makes the final prediction by com-
bining the predictions of individual classifiers using soft voting or hard voting.
FIG. 9.21 Implementation of voting classifier on a dataset that has two classes (Y and N). Voting
classifier combines the predictions of n classifiers using hard voting. Consequently, the final deci-
sion of the voting classifier is Class Y because the total number of classifiers that predicted Class Y
exceeds n/2.