Page 303 - Machine Learning for Subsurface Characterization
P. 303
Classification of sonic wave Chapter 9 265
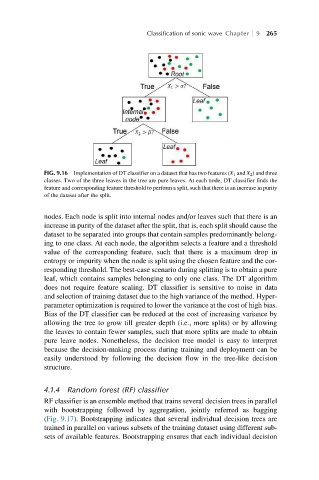
FIG. 9.16 Implementation of DT classifier on a dataset that has two features (X 1 and X 2 ) and three
classes. Two of the three leaves in the tree are pure leaves. At each node, DT classifier finds the
feature and corresponding feature threshold to perform a split, such that there is an increase in purity
of the dataset after the split.
nodes. Each node is split into internal nodes and/or leaves such that there is an
increase in purity of the dataset after the split, that is, each split should cause the
dataset to be separated into groups that contain samples predominantly belong-
ing to one class. At each node, the algorithm selects a feature and a threshold
value of the corresponding feature, such that there is a maximum drop in
entropy or impurity when the node is split using the chosen feature and the cor-
responding threshold. The best-case scenario during splitting is to obtain a pure
leaf, which contains samples belonging to only one class. The DT algorithm
does not require feature scaling. DT classifier is sensitive to noise in data
and selection of training dataset due to the high variance of the method. Hyper-
parameter optimization is required to lower the variance at the cost of high bias.
Bias of the DT classifier can be reduced at the cost of increasing variance by
allowing the tree to grow till greater depth (i.e., more splits) or by allowing
the leaves to contain fewer samples, such that more splits are made to obtain
pure leave nodes. Nonetheless, the decision tree model is easy to interpret
because the decision-making process during training and deployment can be
easily understood by following the decision flow in the tree-like decision
structure.
4.1.4 Random forest (RF) classifier
RF classifier is an ensemble method that trains several decision trees in parallel
with bootstrapping followed by aggregation, jointly referred as bagging
(Fig. 9.17). Bootstrapping indicates that several individual decision trees are
trained in parallel on various subsets of the training dataset using different sub-
sets of available features. Bootstrapping ensures that each individual decision