Page 347 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 347
Section 13.5 Various Rolling Processes and Mills 327
is critical. Extensive electronic and computer controls are used in these operations,
particularly in precision rolling.
Roll Materials. The basic requirements for roll materials are strength and resist-
ance to wear. Common roll materials are cast iron, cast steel, and forged steel; tung-
sten carbide is also used for small-diameter rolls, such as the Working roll in the
cluster mill (Fig. l3.3d). Forged-steel rolls, although more costly than cast rolls,
have higher strength, stiffness, and toughness than cast-iron rolls. Rolls for cold
rolling are ground to a fine finish. For special applications, they also are polished.
Rolls made for cold rolling should not be used for hot rolling, because they may
crack from thermal cycling (heat checking) and spelling (cracking or flaking of sur-
face layers). Recall also from earlier discussions that the elastic modulus of the roll
influences roll deflection and flattening.
Note that the bottom surface of an aluminum beverage can, for example, has
what appear to be longitudinal scratches on it. This is explained by the fact that the
surface is a replica of the surface finish of the roll, which is produced by grinding
(see Fig. 26.2a). In this Way, the rolling direction of the original aluminum sheet also
can be determined easily.
Lubricants. Hot rolling of ferrous alloys usually is carried out Without lubricants,
although graphite may be used. Water-based solutions are used to cool the rolls and
to break up the scale on the rolled material. Nonferrous alloys are hot rolled with a
variety of compounded oils, emulsions, and fatty acids. Cold rolling is carried out
with water-soluble oils or low-viscosity lubricants, such as mineral oils, emulsions,
paraffin, and fatty oils.
13.5 Various Rolling Processes and Mills
Several rolling processes and mills have been developed to produc e a specific family
of product shapes.
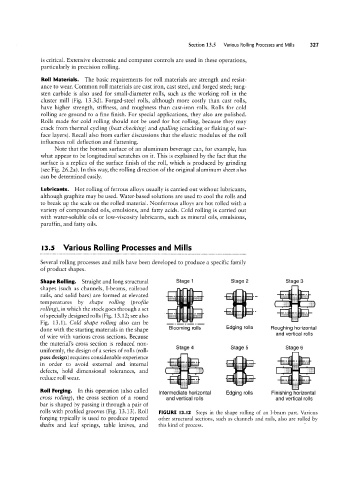
Shape Rolling. Straight and long structural Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3
shapes (such as channels, I-beams, railroad :l l
ill
rails, and solid bars) are formed at elevated llllllll aléla
temperatures by shape rolling (pro/We it Ԥ * H
rolling), in which the stock goes through a set L; algl llia
ill! 'll
of specially designed rolls (Fig. 1312; see also ll la
Fig. 13.1). Cold shape rolling also can be
done with the starting materials in the shape Blooming rolls Edging rolls Ftoughing horizontal
and vertical rolls
of wire with various cross sections. Because
the material’s cross section is reduced non-
Stage 4 Stage 5 Stage 6
uniformly, the design of a series of rolls (roll-
ala
pass design) requires considerable experience Q!! le 1 i
ill lll Ili ill _ l||
in order to avoid external and internal l
defects, hold dimensional tolerances, and
all la ll... ll
reduce roll Wear. alglla
ha
Roll Forging. In this operation (also called Intermediate horizontal Edging rolls Finishing horizontal
cross rolling), the cross section of a round and vertical rolls and vertical rolls
bar is shaped by passing it through a pair of
rolls With profiled grooves (Fig. 13.13). Roll FIGURE l3.l2 Steps in the shape rolling of an I-beam part. Various
forging typically is used to produce tapered other structural sections, such as channels and rails, also are rolled by
shafts and leaf springs, table knives, and this kind of process.