Page 472 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 472
ladle
Induction-heated `
2 Chapter 17 Powder-Metal Processing and Equipment `
Aiomazer
(nitrogen gas) Particle injector
: _
(optional)
I
Mandrel fi; \ Tube
Deposition l \>.
Cha mbe r I f”’!!ng|,§
If
Powder ,rs
recovery "`j'
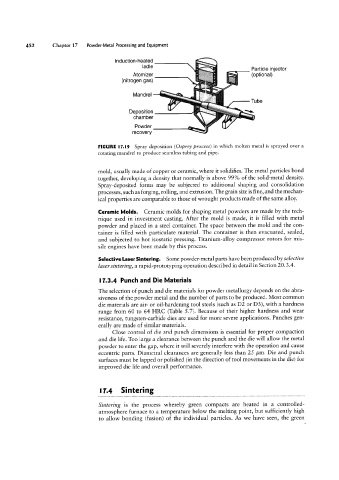
FIGURE l7.l9 Spray deposition (Osprey process) in which molten metal is sprayed over a
rotating mandrel to produce seamless tubing and pipe.
mold, usually made of copper or ceramic, where it solidifies. The metal particles bond
together, developing a density that normally is above 99% of the solid-metal density.
Spray-deposited forms may be subjected to additional shaping and consolidation
processes, such as forging, rolling, and extrusion. The grain size is fine, and the mechan-
ical properties are comparable to those of wrought products made of the same alloy.
Ceramic Molds. Ceramic molds for shaping metal powders are made by the tech-
nique used in investment casting. After the mold is made, it is filled with metal
powder and placed in a steel container. The space between the mold and the con-
tainer is filled with particulate material. The container is then evacuated, sealed,
and subjected to hot isostatic pressing. Titanium-alloy compressor rotors for mis-
sile engines have been made by this process.
Selective Laser Sintering. Some powder-metal parts have been produced by selective
laser sintering, a rapid-prototyping operation described in detail in Section 20.3.4.
l7.3.4 Punch and Die Materials
The selection of punch and die materials for powder metallurgy depends on the abra-
siveness of the powder metal and the number of parts to be produced. Most common
die materials are air- or oil-hardening tool steels (such as D2 or D3), with a hardness
range from 60 to 64 HRC (Table 5.7). Because of their higher hardness and wear
resistance, tungsten-carbide dies are used for more severe applications. Punches gen-
erally are made of similar materials.
Close control of die and punch dimensions is essential for proper compaction
and die life. Too large a clearance between the punch and the die will allow the metal
powder to enter the gap, where it will severely interfere with the operation and cause
eccentric parts. Diametral clearances are generally less than 25 ,um. Die and punch
surfaces must be lapped or polished (in the direction of tool movements in the die) for
improved die life and overall performance.
|1.4 Sintering
Sintering is the process whereby green compacts are heated in a controlled-
atmosphere furnace to a temperature below the melting point, but sufficiently high
to allow bonding (fusion) of the individual particles. As we have seen, the green