Page 499 - Marine Structural Design
P. 499
Chapter 26 Reliability-Based Design and Code Calibration 475
Normal safety cZass: where failure implies negligible risk to human safety, minor danger to the
main part of the platform, minor damages to the environment, certain economic loss.
High safety class: where failure implies risk to the total safety of the platform so as to human
safety and environmental pollution. High economic loss cannot be avoided.
Table 26.2 Recommended Target Safety Level
~
Safety Classes Target Safety
Low PF =loZ p=2.32
~
Normal pF =io-’ p=3.09
High PFz104 p=3.72
26.5.6 Calibration of Safety Factors
Besides the direct use of reliability calculation for tubular joint design, representing a full
probabilistic design, reliability methods can also be used indirectly for the design purpose
based on a calibrated design check with the main goal ofobtaining a uniform safety level. The
main objective of reliability-based calibration of tubular joint design is to achieve the optimal
set of partial safety factors on the basis of a uniform reliability level.
5.0 I
0.04
h
3 4.0
!z
P)
8
TI
c 3.0
=
>.
-
.-
n
m .-
- 2.0
2
1 .o
0.8 1 .o I .2
Resistance Factor
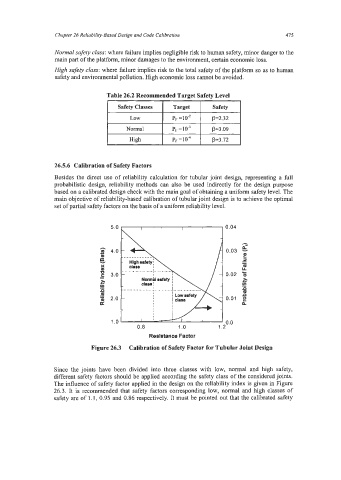
Figure 26.3 Calibration of Safety Factor for Tubular Joint Design
Since the joints have been divided into three classes with low, normal and high safety,
different safety factors should be applied according the safety class of the considered joints.
The influence of safety factor applied in the design on the reliability index is given in Figure
26.3. It is recommended that safety factors corresponding low, normal and high classes of
safety are of 1.1, 0.95 and 0.86 respectively. It must be pointed out that the calibrated safety