Page 446 - Marketing Management
P. 446
DESIGNING AND MANAGING INTEGRATED MARKETING CHANNELS | CHAPTER 15 423
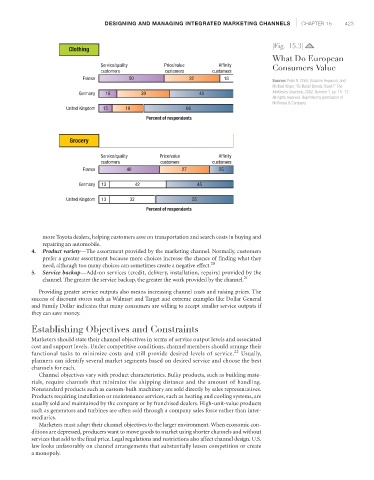
|Fig. 15.3|
Clothing
What Do European
Service/quality Price/value Affinity Consumers Value
customers customers customers
France 50 32 18
Source: Peter N. Child, Suzanne Heywood, and
Michael Kliger, “Do Retail Brands Travel?” The
Germany 16 39 45 McKinsley Quarterly, 2002, Number 1, pp. 11–13.
All rights reserved. Reprinted by permission of
McKinsey & Company.
United Kingdom 15 19 66
Percent of respondents
Grocery
Service/quality Price/value Affinity
customers customers customers
France 40 27 25
Germany 13 42 45
United Kingdom 13 32 55
Percent of respondents
more Toyota dealers, helping customers save on transportation and search costs in buying and
repairing an automobile.
4. Product variety—The assortment provided by the marketing channel. Normally, customers
prefer a greater assortment because more choices increase the chance of finding what they
need, although too many choices can sometimes create a negative effect. 20
5. Service backup—Add-on services (credit, delivery, installation, repairs) provided by the
channel. The greater the service backup, the greater the work provided by the channel. 21
Providing greater service outputs also means increasing channel costs and raising prices. The
success of discount stores such as Walmart and Target and extreme examples like Dollar General
and Family Dollar indicates that many consumers are willing to accept smaller service outputs if
they can save money.
Establishing Objectives and Constraints
Marketers should state their channel objectives in terms of service output levels and associated
cost and support levels. Under competitive conditions, channel members should arrange their
functional tasks to minimize costs and still provide desired levels of service. 22 Usually,
planners can identify several market segments based on desired service and choose the best
channels for each.
Channel objectives vary with product characteristics. Bulky products, such as building mate-
rials, require channels that minimize the shipping distance and the amount of handling.
Nonstandard products such as custom-built machinery are sold directly by sales representatives.
Products requiring installation or maintenance services, such as heating and cooling systems, are
usually sold and maintained by the company or by franchised dealers. High-unit-value products
such as generators and turbines are often sold through a company sales force rather than inter-
mediaries.
Marketers must adapt their channel objectives to the larger environment. When economic con-
ditions are depressed, producers want to move goods to market using shorter channels and without
services that add to the final price. Legal regulations and restrictions also affect channel design. U.S.
law looks unfavorably on channel arrangements that substantially lessen competition or create
amonopoly.