Page 139 - Marks Calculation for Machine Design
P. 139
P1: Sanjay
January 4, 2005
Brown˙C02
Brown.cls
B
A 16:18 BEAMS w 121
L
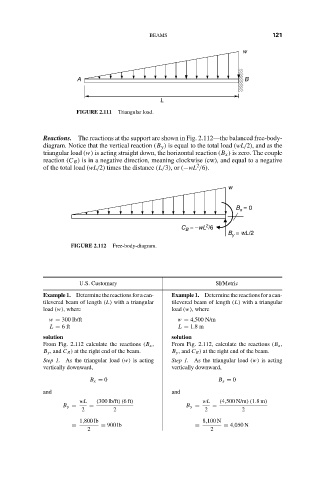
FIGURE 2.111 Triangular load.
Reactions. The reactions at the support are shown in Fig. 2.112—the balanced free-body-
diagram. Notice that the vertical reaction (B y ) is equal to the total load (wL/2), and as the
triangular load (w) is acting straight down, the horizontal reaction (B x ) is zero. The couple
reaction (C B ) is in a negative direction, meaning clockwise (cw), and equal to a negative
2
of the total load (wL/2) times the distance (L/3), or (−wL /6).
w
B = 0
x
2
C = –wL /6
B
B = wL/2
y
FIGURE 2.112 Free-body-diagram.
U.S. Customary SI/Metric
Example 1. Determine the reactions for a can- Example 1. Determine the reactions for a can-
tilevered beam of length (L) with a triangular tilevered beam of length (L) with a triangular
load (w), where load (w), where
w = 300 lb/ft w = 4,500 N/m
L = 6ft L = 1.8 m
solution solution
From Fig. 2.112 calculate the reactions (B x , From Fig. 2.112, calculate the reactions (B x ,
B y , and C B ) at the right end of the beam. B y , and C B ) at the right end of the beam.
Step 1. As the triangular load (w) is acting Step 1. As the triangular load (w) is acting
vertically downward, vertically downward,
B x = 0 B x = 0
and and
wL (300 lb/ft)(6ft) wL (4,500 N/m)(1.8m)
B y = = B y = =
2 2 2 2
1,800 lb 8,100 N
= = 900 lb = = 4,050 N
2 2