Page 323 - Marks Calculation for Machine Design
P. 323
P1: Shashi
January 4, 2005
15:4
Brown˙C07
Brown.cls
FATIGUE AND DYNAMIC DESIGN
305
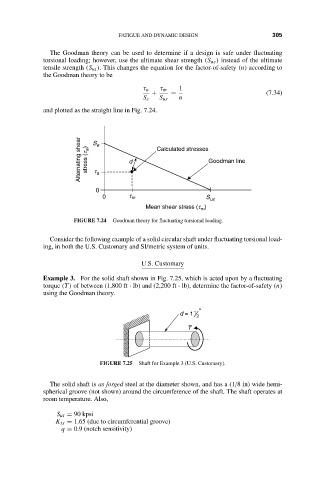
The Goodman theory can be used to determine if a design is safe under fluctuating
torsional loading; however, use the ultimate shear strength (S us ) instead of the ultimate
tensile strength (S ut ). This changes the equation for the factor-of-safety (n) according to
the Goodman theory to be
τ a τ m 1
+ = (7.34)
S e S us n
and plotted as the straight line in Fig. 7.24.
Alternating shear stress (t a ) S e a d Calculated stresses Goodman line
t
0
0 t m S us
Mean shear stress (t )
m
FIGURE 7.24 Goodman theory for fluctuating torsional loading.
Consider the following example of a solid circular shaft under fluctuating torsional load-
ing, in both the U.S. Customary and SI/metric system of units.
U.S. Customary
Example 3. For the solid shaft shown in Fig. 7.25, which is acted upon by a fluctuating
torque (T ) of between (1,800 ft · lb) and (2,200 ft · lb), determine the factor-of-safety (n)
using the Goodman theory.
1 "
d = 1
2
T
FIGURE 7.25 Shaft for Example 3 (U.S. Customary).
The solid shaft is as forged steel at the diameter shown, and has a (1/8 in) wide hemi-
spherical groove (not shown) around the circumference of the shaft. The shaft operates at
room temperature. Also,
S ut = 90 kpsi
K ts = 1.65 (due to circumferential groove)
q = 0.9 (notch sensitivity)