Page 79 - Marks Calculation for Machine Design
P. 79
P1: Sanjay
January 4, 2005
Brown˙C02
Brown.cls
A 16:18 BEAMS w 61
B
L
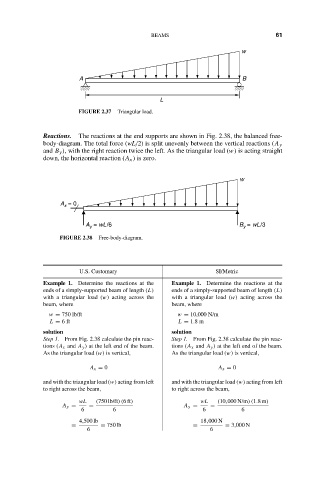
FIGURE 2.37 Triangular load.
Reactions. The reactions at the end supports are shown in Fig. 2.38, the balanced free-
body-diagram. The total force (wL/2) is split unevenly between the vertical reactions (A y
and B y ), with the right reaction twice the left. As the triangular load (w) is acting straight
down, the horizontal reaction (A x ) is zero.
w
A = 0
x
A = wL/6 B = wL/3
y
y
FIGURE 2.38 Free-body-diagram.
U.S. Customary SI/Metric
Example 1. Determine the reactions at the Example 1. Determine the reactions at the
ends of a simply-supported beam of length (L) ends of a simply-supported beam of length (L)
with a triangular load (w) acting across the with a triangular load (w) acting across the
beam, where beam, where
w = 750 lb/ft w = 10,000 N/m
L = 6ft L = 1.8 m
solution solution
Step 1. From Fig. 2.38 calculate the pin reac- Step 1. From Fig. 2.38 calculate the pin reac-
tions (A x and A y ) at the left end of the beam. tions (A x and A y ) at the left end of the beam.
As the triangular load (w) is vertical, As the triangular load (w) is vertical,
A x = 0 A x = 0
and with the triangular load (w) acting from left and with the triangular load (w) acting from left
to right across the beam, to right across the beam,
wL (750 lb/ft)(6ft) wL (10,000 N/m)(1.8m)
A y = = A y = =
6 6 6 6
4,500 lb 18,000 N
= = 750 lb = = 3,000 N
6 6