Page 207 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 207
6.5 Elastic Properties of Materials • 179
EXAMPLE PROBLEM 6.2
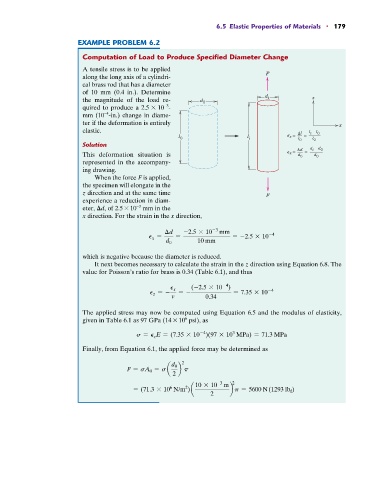
Computation of Load to Produce Specified Diameter Change
A tensile stress is to be applied
along the long axis of a cylindri- F
cal brass rod that has a diameter
of 10 mm (0.4 in.). Determine
the magnitude of the load re- d 0 d i z
-3
quired to produce a 2.5 * 10 -
-4
mm (10 -in.) change in diame-
ter if the deformation is entirely x
elastic. l – l
l 0 l i z = l = i l 0
0 0
Solution
d – d 0
i
This deformation situation is x = d 0 = d 0
represented in the accompany-
ing drawing.
When the force F is applied,
the specimen will elongate in the
z direction and at the same time F
experience a reduction in diam-
-3
eter, ≤d, of 2.5 * 10 mm in the
x direction. For the strain in the x direction,
-3
d -2.5 * 10 mm
P x = = = -2.5 * 10 -4
d 0 10 mm
which is negative because the diameter is reduced.
It next becomes necessary to calculate the strain in the z direction using Equation 6.8. The
value for Poisson’s ratio for brass is 0.34 (Table 6.1), and thus
-4
(-2.5 * 10 )
P x -4
P z = - = - = 7.35 * 10
v 0.34
The applied stress may now be computed using Equation 6.5 and the modulus of elasticity,
6
given in Table 6.1 as 97 GPa (14 * 10 psi), as
-4
3
s = P z E = (7.35 * 10 )(97 * 10 MPa) = 71.3 MPa
Finally, from Equation 6.1, the applied force may be determined as
2
d 0
F = sA 0 = s a b p
2
-3
10 * 10 m 2
6 2
= (71.3 * 10 N/m ) a b p = 5600 N (1293 lb f )
2