Page 212 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 212
184 • Chapter 6 / Mechanical Properties of Metals
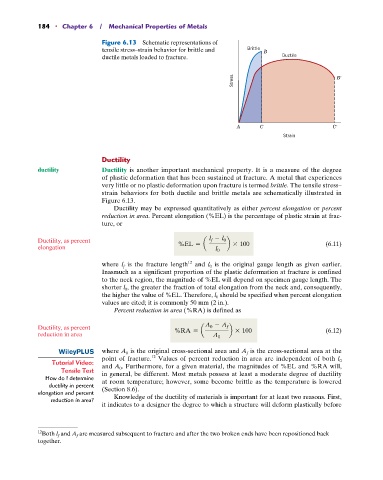
Figure 6.13 Schematic representations of
tensile stress–strain behavior for brittle and Brittle B
ductile metals loaded to fracture. Ductile
Stress B
A C C
Strain
Ductility
ductility Ductility is another important mechanical property. It is a measure of the degree
of plastic deformation that has been sustained at fracture. A metal that experiences
very little or no plastic deformation upon fracture is termed brittle. The tensile stress–
strain behaviors for both ductile and brittle metals are schematically illustrated in
Figure 6.13.
Ductility may be expressed quantitatively as either percent elongation or percent
reduction in area. Percent elongation (%EL) is the percentage of plastic strain at frac-
ture, or
Ductility, as percent l f - l 0 (6.11)
elongation %EL = a l 0 b * 100
is the fracture length 12 is the original gauge length as given earlier.
where l f and l 0
Inasmuch as a significant proportion of the plastic deformation at fracture is confined
to the neck region, the magnitude of %EL will depend on specimen gauge length. The
shorter l 0 , the greater the fraction of total elongation from the neck and, consequently,
the higher the value of %EL. Therefore, l 0 should be specified when percent elongation
values are cited; it is commonly 50 mm (2 in.).
Percent reduction in area (%RA) is defined as
Ductility, as percent A 0 - A f (6.12)
reduction in area %RA = a A 0 b * 100
where A 0 is the original cross-sectional area and A f is the cross-sectional area at the
point of fracture. 12 Values of percent reduction in area are independent of both l 0
Tutorial Video: and A 0 . Furthermore, for a given material, the magnitudes of %EL and %RA will,
Tensile Test in general, be different. Most metals possess at least a moderate degree of ductility
How do I determine at room temperature; however, some become brittle as the temperature is lowered
ductility in percent (Section 8.6).
elongation and percent Knowledge of the ductility of materials is important for at least two reasons. First,
reduction in area?
it indicates to a designer the degree to which a structure will deform plastically before
12 Both l f and A f are measured subsequent to fracture and after the two broken ends have been repositioned back
together.