Page 42 - Mechanical design of microresonators _ modeling and applications
P. 42
0-07-145538-8_CH01_41_08/30/05
Design at Resonance of Mechanical Microsystems
Design at Resonance of Mechanical Microsystems 41
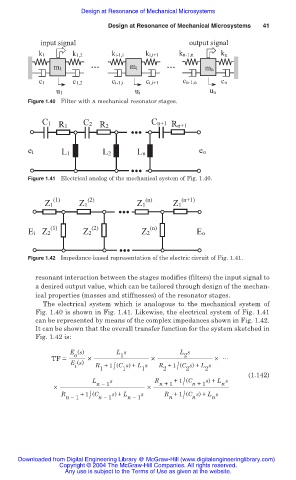
input signal output signal
k1 k1,2 ki-1,i ki,i+1 kn-1,n kn
m1 mi mn
c1 c1,2 ci-1,i ci,i+1 cn-1,n cn
u1 ui un
Figure 1.40 Filter with n mechanical resonator stages.
C1 C2 Cn+1
R1 R2 Rn+1
ei L1 L2 Ln eo
Figure 1.41 Electrical analog of the mechanical system of Fig. 1.40.
(1) (2) (n) (n+1)
Z1 Z1 Z1 Z1
(1) (2) (n)
Ei Z2 Z2 Z2 Eo
Figure 1.42 Impedance-based representation of the electric circuit of Fig. 1.41.
resonant interaction between the stages modifies (filters) the input signal to
a desired output value, which can be tailored through design of the mechan-
ical properties (masses and stiffnesses) of the resonator stages.
The electrical system which is analogous to the mechanical system of
Fig. 1.40 is shown in Fig. 1.41. Likewise, the electrical system of Fig. 1.41
can be represented by means of the complex impedances shown in Fig. 1.42.
It can be shown that the overall transfer function for the system sketched in
Fig. 1.42 is:
E (s) L s L s
o
1
2
TF = × × × 썳
E (s)
2 /
1 /
i R +1 (C s) + L s R +1 (C s) + L s
2
1
2
1
(1.142)
+1 (C
L n 1 s R n +1 / n +1 s) + L s
n
× ×
n /
+1 (C
R n 1 / n 1 s) + L n 1 s R +1 (C s) + L s
n
n
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.