Page 46 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 46
STRENGTHS OF MATERIALS 35
I .5.2 Leaf and laminated leaf springs
Leaf springs
A leaf spring consists basically of a beam, usually of flat
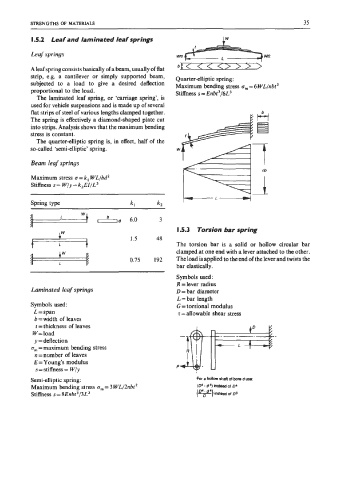
strip, e.g. a cantilever or simply supported beam, Quarter-elliptic spring:
subjected to a load to give a desired deflection Maximum bending stress om= 6 WLfnbt’
proportional to the load. Stiffness s = Enbt3/6L3
The laminated leaf spring, or ‘camage spring’, is
used for vehicle suspensions and is made up of several
flat strips of steel of various lengths clamped together.
The spring is effectively a diamond-shaped plate cut
into strips. Analysis shows that the maximum bending
stress is constant.
The quarter-elliptic spring is, in effect, half of the
so-called ’semi-elliptic’ spring.
Beam leaf springs
Maximum stress u=k, WLfbd’
Stiffness s= Wfy=k2EIfL3
Spring type kl k2
id+ b 6.0 3
-d
I .5.3 Torsion bar spring
1.5 48
The torsion bar is a solid or hollow circular bar
clamped at one end with a lever attached to the other.
0.75 192 The load is applied to the end of the lever and twists the
bar elastically.
Symbols used:
R =lever radius
Laminated leaf springs D = bar diameter
L = bar length
Symbols used: G = torsional modulus
L = span 7 =allowable shear stress
b = width of leaves
t = thickness of leaves
W = load
y = deflection
urn =maximum bending stress
n =number of leaves
E =Young’s modulus
s = stiffness = WJy P
Semi-elliptic spring: For a hollow shafl of bore dum:
Maximum bending stress u, = 3 WL/2nbt2 (D4 - d insteed of 04
of
insteed
Stiffness s = 8Enbt3 J3 L3 (v) 03