Page 16 - Mechanical Engineers Reference Book
P. 16
Dynamics of rigid bodies 115
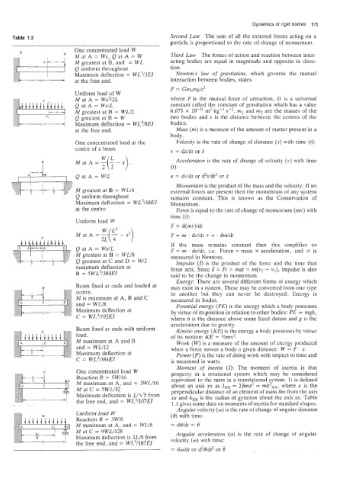
Table 1.2 Second Law The sum of all the external forces acting on a
particle is proportional to the rate of change of momentum.
B One concentrated load W Third Law The forces of action and reaction between inter-
MatA= Wx,QatA= W
M greatest at B, and = WL acting bodies are equal in magnitude and opposite in direc-
Q uniform throughout tion.
Maximum deflection = WL313EI Newton's law of gravitation, which governs the mutual
- L at the free end. interaction between bodies, states
F = Gmlm21x2
Uniform load of W
M at A = Wx212L where F is the mutual force of attraction, G is a universal
Q at A = WxlL constant called the constant of gravitation which has a value
M greatest at B = WLl2 6.673 X lo-" m3 kg-l sC2, ml and m2 are the masses of the
Q greatest at B = W two bodies and x is the distance between the centres of the
--L+ Maximum deflection = WL318EI bodies.
at the free end. Mass (m) is a measure of the amount of matter present in a
body.
One concentrated load at the Velocity is the rate of change of distance (n) with time (t):
centre oi a beam v = dxldt or k
Mat A ="(& - x), Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity (v) with time
22 (4 :
Q at A = W12 a = dvldt or d2xld? or x
Momentum is the product of the mass and the velocity. If no
M greatest at B = WLl4 external forces are present then the momentum of any system
Q uniform throughout remains constant. This is known as the Conservation of
Maximum deflection = WL3148El Momentum.
at the centre Force is equal to the rate of change of momentum (mv) with
time (t):
Uniform load W
F = d(mv)/dt
F = m . dvldt + v . dmldt
W
If the mass remains constant then this simplifies to
Q at A = WxIL F = m dvldt, i.e. Force = mass X acceleration, and it is
M greatest at B = WLl8 measured in Newtons.
Q greatest at C and D = W12 Impulse (I) is the product of the force and the time that
maximum deflection at force acts. Since I = Ft = mat = m(v2 - vl), impulse is also
B = 5WL3/384EI said to be the change in momentum.
Energy: There are several different forms of energy which
Beam fixed at ends and loaded at may exist in a system. These may be converted from one type
centre. to another but they can never be destroyed. Energy is
M is maximum at A, B and C measured in Joules.
and = WL18. Potential energy (PE) is the energy which a body possesses
Maximum deflection at by virtue of its position in relation to other bodies: PE = mgh,
C = WL3/192EI where h is the distance above some fixed datum and g is the
acceleration due to gravity.
Beam fixed at ends with uniform Kinetic energy (KE) is the energy a body possesses by virtue
load. of its motion: KE = %mv2.
M maximum at A and B Work (w) a measure of the amount of energy produced
is
and = WLl12 when a force moves a body a given distance: W = F . x.
Maximum deflection at Power (P) is the rate of doing work with respect to time and
C = WL31384EI is measured in watts.
Moment of inertia (I): The moment of inertia is that
One concentrated load W property in a rotational system which may be considered
Reaction R = SWl16
'' M maxiinum at A, and = 3WLl16 equivalent to the mass in a translational system. It is defined
I
about an axis xx as Ixx = Smx' = mk2m, where x is the
C M at C = 5WLl32
Maximum deflection is LIVS from perpendicular distance of an element of mass 6m from the axis
xx and kxx is the radius of gyration about the axis xx. Table
7 1.1 gives some data on moments of inertia for standard shapes.
the free end, and = WL31107EI
Angular velocity (w) is the rate of change of angular distance
Uniform load W (0) with time:
Reaction R = 3Wl8
M maximum at A, and = WLI8 = d0ldt = 6
M at C = 9WL1128 Angular acceleration (a) is the rate of change of acgular
Maximum deflection is 3L18 from velocity (0) with time:
the free end, and = WL31187EI
= dwldt or d28/d$ or 0