Page 566 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 2)
P. 566
4 Alternating-Current Servomotors 557
K v
Ta 309 rad/s 2953 rpm (18)
m
RB KK E
am
T
and the temperature rise is
T (2 C/W) (175 W) 350 C (19)
This temperature rise is greater than the 155 C maximum allowable winding temperature.
Thus the motor cannot be operated at peak torque indefinitely. The ambient temperature
should be added to the temperature rise to arrive at the operating temperature of the winding.
4 ALTERNATING-CURRENT SERVOMOTORS
Alternating-current servomotors are used in applications requiring smooth speed control.
These motors find widespread use in stationary industrial applications due to the ready avail-
ability of ac power. 16,17 In a majority of these applications, two-phase ac servomotors are
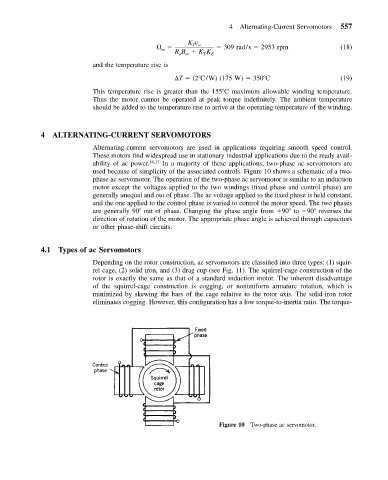
used because of simplicity of the associated controls. Figure 10 shows a schematic of a two-
phase ac servomotor. The operation of the two-phase ac servomotor is similar to an induction
motor except the voltages applied to the two windings (fixed phase and control phase) are
generally unequal and out of phase. The ac voltage applied to the fixed phase is held constant,
and the one applied to the control phase is varied to control the motor speed. The two phases
are generally 90 out of phase. Changing the phase angle from 90 to 90 reverses the
direction of rotation of the motor. The appropriate phase angle is achieved through capacitors
or other phase-shift circuits.
4.1 Types of ac Servomotors
Depending on the rotor construction, ac servomotors are classified into three types: (1) squir-
rel cage, (2) solid iron, and (3) drag cup (see Fig. 11). The squirrel-cage construction of the
rotor is exactly the same as that of a standard induction motor. The inherent disadvantage
of the squirrel-cage construction is cogging, or nonuniform armature rotation, which is
minimized by skewing the bars of the cage relative to the rotor axis. The solid-iron rotor
eliminates cogging. However, this configuration has a low torque-to-inertia ratio. The torque-
Figure 10 Two-phase ac servomotor.