Page 308 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 308
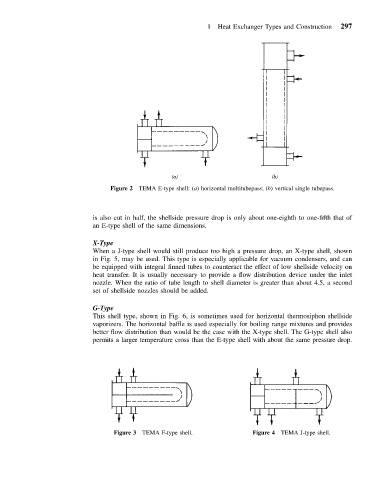
1 Heat Exchanger Types and Construction 297
Figure 2 TEMA E-type shell: (a) horizontal multitubepass; (b) vertical single tubepass.
is also cut in half, the shellside pressure drop is only about one-eighth to one-fifth that of
an E-type shell of the same dimensions.
X-Type
When a J-type shell would still produce too high a pressure drop, an X-type shell, shown
in Fig. 5, may be used. This type is especially applicable for vacuum condensers, and can
be equipped with integral finned tubes to counteract the effect of low shellside velocity on
heat transfer. It is usually necessary to provide a flow distribution device under the inlet
nozzle. When the ratio of tube length to shell diameter is greater than about 4.5, a second
set of shellside nozzles should be added.
G-Type
This shell type, shown in Fig. 6, is sometimes used for horizontal thermosiphon shellside
vaporizers. The horizontal baffle is used especially for boiling range mixtures and provides
better flow distribution than would be the case with the X-type shell. The G-type shell also
permits a larger temperature cross than the E-type shell with about the same pressure drop.
Figure 3 TEMA F-type shell. Figure 4 TEMA J-type shell.