Page 313 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 313
302 Heat Exchangers, Vaporizers, Condensers
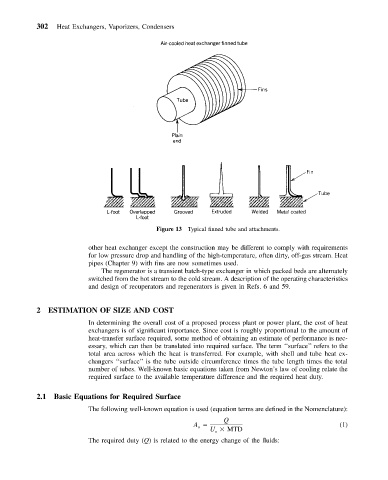
Figure 13 Typical finned tube and attachments.
other heat exchanger except the construction may be different to comply with requirements
for low pressure drop and handling of the high-temperature, often dirty, off-gas stream. Heat
pipes (Chapter 9) with fins are now sometimes used.
The regenerator is a transient batch-type exchanger in which packed beds are alternately
switched from the hot stream to the cold stream. A description of the operating characteristics
and design of recuperators and regenerators is given in Refs. 6 and 59.
2 ESTIMATION OF SIZE AND COST
In determining the overall cost of a proposed process plant or power plant, the cost of heat
exchangers is of significant importance. Since cost is roughly proportional to the amount of
heat-transfer surface required, some method of obtaining an estimate of performance is nec-
essary, which can then be translated into required surface. The term ‘‘surface’’ refers to the
total area across which the heat is transferred. For example, with shell and tube heat ex-
changers ‘‘surface’’ is the tube outside circumference times the tube length times the total
number of tubes. Well-known basic equations taken from Newton’s law of cooling relate the
required surface to the available temperature difference and the required heat duty.
2.1 Basic Equations for Required Surface
The following well-known equation is used (equation terms are defined in the Nomenclature):
Q
A (1)
o
U MTD
o
The required duty (Q) is related to the energy change of the fluids: