Page 311 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 311
300 Heat Exchangers, Vaporizers, Condensers
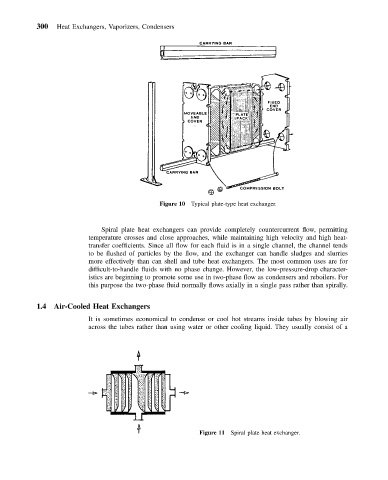
Figure 10 Typical plate-type heat exchanger.
Spiral plate heat exchangers can provide completely countercurrent flow, permitting
temperature crosses and close approaches, while maintaining high velocity and high heat-
transfer coefficients. Since all flow for each fluid is in a single channel, the channel tends
to be flushed of particles by the flow, and the exchanger can handle sludges and slurries
more effectively than can shell and tube heat exchangers. The most common uses are for
difficult-to-handle fluids with no phase change. However, the low-pressure-drop character-
istics are beginning to promote some use in two-phase flow as condensers and reboilers. For
this purpose the two-phase fluid normally flows axially in a single pass rather than spirally.
1.4 Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
It is sometimes economical to condense or cool hot streams inside tubes by blowing air
across the tubes rather than using water or other cooling liquid. They usually consist of a
Figure 11 Spiral plate heat exchanger.