Page 139 -
P. 139
4.2 Theoretical Analysis I – Optical Torque 129
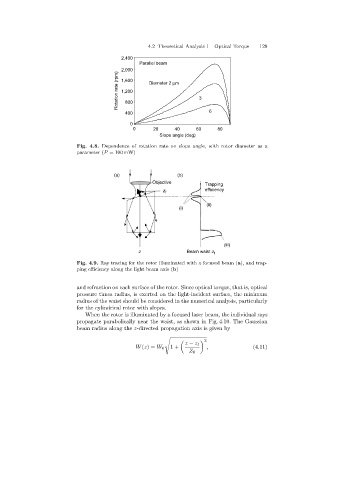
2,400
Parallel beam
2,000
Rotation rate (rpm) 1,600 Diameter 2 mm 3
1,200
800
400 6
0
0 20 40 60 80
Slope angle (deg)
Fig. 4.8. Dependence of rotation rate on slope angle, with rotor diameter as a
parameter (P = 100 mW)
(a) (b)
Objective
Trapping
z f efficiency
(ii)
(i)
(iii)
z Beam waist z f
Fig. 4.9. Ray tracing for the rotor illuminated with a focused beam (a), and trap-
ping efficiency along the light beam axis (b)
and refraction on each surface of the rotor. Since optical torque, that is, optical
pressure times radius, is exerted on the light-incident surface, the minimum
radius of the waist should be considered in the numerical analysis, particularly
for the cylindrical rotor with slopes.
When the rotor is illuminated by a focused laser beam, the individual rays
propagate parabolically near the waist, as shown in Fig. 4.10. The Gaussian
beam radius alongthe z-directed propagation axis is given by
2
z − z f
1+ , (4.11)
W(z)= W 0
Z 0