Page 259 - A Practical Guide from Design Planning to Manufacturing
P. 259
Circuit Design 231
Poly
gate
_
Source Drain
+ _ +_
+ _ _
+ _ + _
+
Neutron
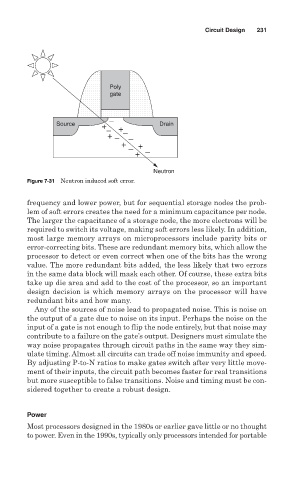
Figure 7-31 Neutron induced soft error.
frequency and lower power, but for sequential storage nodes the prob-
lem of soft errors creates the need for a minimum capacitance per node.
The larger the capacitance of a storage node, the more electrons will be
required to switch its voltage, making soft errors less likely. In addition,
most large memory arrays on microprocessors include parity bits or
error-correcting bits. These are redundant memory bits, which allow the
processor to detect or even correct when one of the bits has the wrong
value. The more redundant bits added, the less likely that two errors
in the same data block will mask each other. Of course, these extra bits
take up die area and add to the cost of the processor, so an important
design decision is which memory arrays on the processor will have
redundant bits and how many.
Any of the sources of noise lead to propagated noise. This is noise on
the output of a gate due to noise on its input. Perhaps the noise on the
input of a gate is not enough to flip the node entirely, but that noise may
contribute to a failure on the gate’s output. Designers must simulate the
way noise propagates through circuit paths in the same way they sim-
ulate timing. Almost all circuits can trade off noise immunity and speed.
By adjusting P-to-N ratios to make gates switch after very little move-
ment of their inputs, the circuit path becomes faster for real transitions
but more susceptible to false transitions. Noise and timing must be con-
sidered together to create a robust design.
Power
Most processors designed in the 1980s or earlier gave little or no thought
to power. Even in the 1990s, typically only processors intended for portable