Page 134 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 134
114 STANDARD MICROELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGIES
gates to define. The newest type of component is the programmable analogue array (PAA)
device, and these may well become increasingly important in sensing applications in which
the design of an operational amplifier circuit can be set and reset through I/O ports.
It should be noted that this classification of devices into hardware and software
programming is not universally accepted. Sometimes, it may be more useful to distinguish
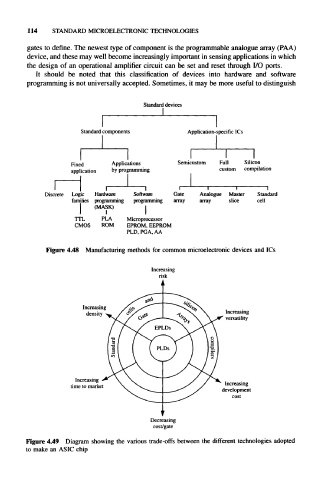
Standard devices
Standard components Application-specific ICs
Fixed Applications Semicustom Full Silicon
application by programming custom compilation
1 1 1 1 i l l I
Discrete Logic Hardware Software Gate Analogue Master Standard
fam lies programming programming array array slice cell
(MASK)
1
n"L PLA Microprocessor
OMOS ROM EPROM, EEPROM
PLD, PGA, AA
Figure 4.48 Manufacturing methods for common microelectronic devices and ICs
Increasing
risk
Increasing
density Increasing
versatility
Increasing
time to market Increasing
development
cost
V
Decreasing
cost/gate
Figure 4.49 Diagram showing the various trade-offs between the different technologies adopted
to make an ASIC chip