Page 130 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 130
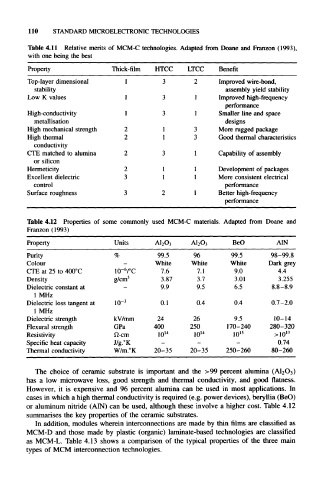
110 STANDARD MICROELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGIES
Table 4.11 Relative merits of MCM-C technologies, Adapted from Doane and Franzon (1993),
with one being the best
Property Thick-film HTCC LTCC Benefit
Top-layer dimensional 1 3 2 Improved wire-bond,
stability assembly yield stability
Low K values 1 3 1 Improved high-frequency
performance
High-conductivity 1 3 1 Smaller line and space
metallisation designs
High mechanical strength 2 1 3 More rugged package
High thermal 2 1 3 Good thermal characteristics
conductivity
CTE matched to alumina 2 3 1 Capability of assembly
or silicon
Hermeticity 2 1 1 Development of packages
Excellent dielectric 3 1 1 More consistent electrical
control performance
Surface roughness 3 2 1 Better high-frequency
performance
Table 4.12 Properties of some commonly used MCM-C materials. Adapted from Doane and
Franzon (1993)
Property Units AI 2O 3 AI 2O 3 BeO A1N
Purity % 99.5 96 99.5 98-99.8
Colour - White White White Dark grey
6
CTE at 25 to 400°C 10- /°C 7.6 7.1 9.0 4.4
3
Density g/cm 3.87 3.7 3.01 3.255
Dielectric constant at - 9.9 9.5 6.5 8.8-8.9
1 MHz –3
Dielectric loss tangent at 10 0.1 0.4 0.4 0.7-2.0
1 MHz
Dielectric strength kV/mm 24 26 9.5 10-14
Flexural strength GPa 400 250 170-240 280-320
Resistivity ft-cm 10 14 10 14 10 15 >10 13
Specific heat capacity J/g.°K - - - 0.74
Thermal conductivity W/m.°K 20-35 20-35 250-260 80-260
The choice of ceramic substrate is important and the >99 percent alumina
has a low microwave loss, good strength and thermal conductivity, and good flatness.
However, it is expensive and 96 percent alumina can be used in most applications. In
cases in which a high thermal conductivity is required (e.g. power devices), beryllia (BeO)
or aluminum nitride (A1N) can be used, although these involve a higher cost. Table 4.12
summarises the key properties of the ceramic substrates.
In addition, modules wherein interconnections are made by thin films are classified as
MCM-D and those made by plastic (organic) laminate-based technologies are classified
as MCM-L. Table 4.13 shows a comparison of the typical properties of the three main
types of MCM interconnection technologies.