Page 169 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 169
SACRIFICIAL LAYER TECHNOLOGY 149
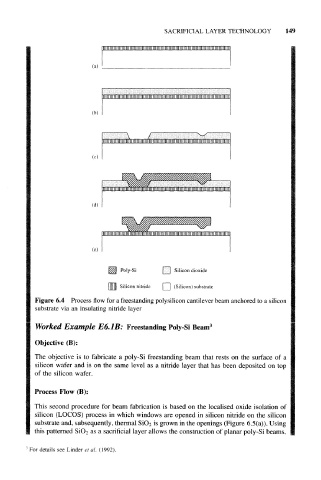
(a)
(b)
(c)
Poly-Si Silicon dioxide
Silicon nitride (Silicon) substrate
Figure 6.4 Process flow for a freestanding polysilicon cantilever beam anchored to a silicon
substrate via an insulating nitride layer
Worked Example E6.1B: Freestanding Poly-Si Beam 3
Objective (B):
The objective is to fabricate a poly-Si freestanding beam that rests on the surface of a
silicon wafer and is on the same level as a nitride layer that has been deposited on top
of the silicon wafer.
Process Flow (B):
This second procedure for beam fabrication is based on the localised oxide isolation of
silicon (LOCOS) process in which windows are opened in silicon nitride on the silicon
substrate and, subsequently, thermal SiO2 is grown in the openings (Figure 6.5(a)). Using
this patterned SiO 2 as a sacrificial layer allows the construction of planar poly-Si beams.
For details see Linder et al. (1992).