Page 238 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 238
218 MICROSTEREOLITHOGRAPHY FOR MEMS
Pumping
Piezoelectric disk chamber
Ball valves
500 1000 1500 2000 2500
Delivery head (mm)
(b)
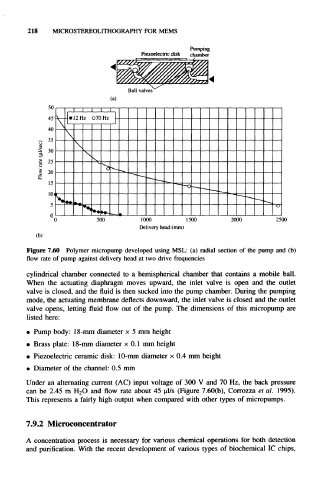
Figure 7.60 Polymer micropump developed using MSL: (a) radial section of the pump and (b)
flow rate of pump against delivery head at two drive frequencies
cylindrical chamber connected to a hemispherical chamber that contains a mobile ball.
When the actuating diaphragm moves upward, the inlet valve is open and the outlet
valve is closed, and the fluid is then sucked into the pump chamber. During the pumping
mode, the actuating membrane deflects downward, the inlet valve is closed and the outlet
valve opens, letting fluid flow out of the pump. The dimensions of this micropump are
listed here:
• Pump body: 18-mm diameter x 5 mm height
• Brass plate: 18-mm diameter x 0.1 mm height
• Piezoelectric ceramic disk: 10-mm diameter x 0.4 mm height
• Diameter of the channel: 0.5 mm
Under an alternating current (AC) input voltage of 300 V and 70 Hz, the back pressure
can be 2.45 m H 2O and flow rate about 45 ul/s (Figure 7.60(b), Corrozza et al. 1995).
This represents a fairly high output when compared with other types of micropumps.
7.9.2 Microconcentrator
A concentration process is necessary for various chemical operations for both detection
and purification. With the recent development of various types of biochemical IC chips,