Page 270 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 270
250 MICROSENSORS
If we assume that these microstructures are made of a uniform, homogeneous, and
elastic material, we can apply a simple theory to describe the way in which they deform
when a mechanical load is applied, such as a force, torque, stress, or pressure.
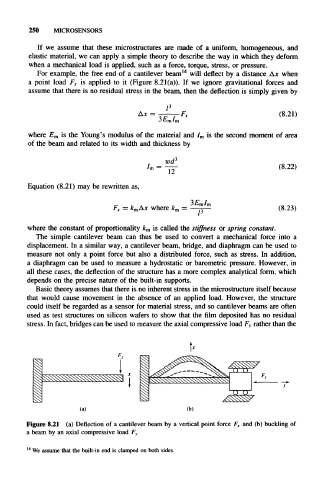
For example, the free end of a cantilever beam 14 will deflect by a distance AJC when
a point load F x is applied to it (Figure 8.21 (a)). If we ignore gravitational forces and
assume that there is no residual stress in the beam, then the deflection is simply given by
3
/
AJC = (8.21)
3£ m/ n
where E m is the Young's modulus of the material and l m is the second moment of area
of the beam and related to its width and thickness by
3
wd
I m = (8.22)
Equation (8.21) may be rewritten as,
3E mI n
F x = k m Ax where k m = (8.23)
where the constant of proportionality k m is called the stiffness or spring constant.
The simple cantilever beam can thus be used to convert a mechanical force into a
displacement. In a similar way, a cantilever beam, bridge, and diaphragm can be used to
measure not only a point force but also a distributed force, such as stress. In addition,
a diaphragm can be used to measure a hydrostatic or barometric pressure. However, in
all these cases, the deflection of the structure has a more complex analytical form, which
depends on the precise nature of the built-in supports.
Basic theory assumes that there is no inherent stress in the microstructure itself because
that would cause movement in the absence of an applied load. However, the structure
could itself be regarded as a sensor for material stress, and so cantilever beams are often
used as test structures on silicon wafers to show that the film deposited has no residual
rather than the
stress. In fact, bridges can be used to measure the axial compressive load F y
Figure 8.21 (a) Deflection of a cantilever beam by a vertical point force F x and (b) buckling of
a beam by an axial compressive load F y
14
We assume that the built-in end is clamped on both sides.