Page 312 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 312
292 MICROSENSORS
8.6.2 Potentiometric Devices
There is a class of field-effect gas sensors based on metal-insulator semiconductor struc-
tures in which the gate is made from a gas-sensitive catalytic metal (Lundstrom 1981).
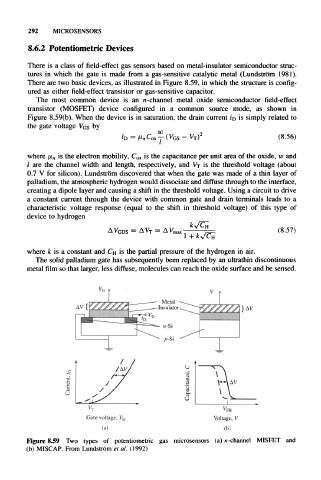
There are two basic devices, as illustrated in Figure 8.59, in which the structure is config-
ured as either field-effect transistor or gas-sensitive capacitor.
The most common device is an n -channel metal oxide semiconductor field-effect
transistor (MOSFET) device configured in a common source mode, as shown in
Figure 8.59(b). When the device is in saturation, the drain current I'D is simply related to
the gate voltage V GS by
W) 2 (8.56)
is the electron is the capacitance per unit area of the oxide, u; and
where ii n mobility, C ox
/ are the channel width and length, respectively, and VT is the threshold voltage (about
0.7 V for silicon). Lundstrom discovered that when the gate was made of a thin layer of
palladium, the atmospheric hydrogen would dissociate and diffuse through to the interface,
creating a dipole layer and causing a shift in the threshold voltage. Using a circuit to drive
a constant current through the device with common gate and drain terminals leads to a
characteristic voltage response (equal to the shift in threshold voltage) of this type of
device to hydrogen
i r^r~
A VGDS = A W = A V max " (8.57)
where k is a constant and C H is the partial pressure of the hydrogen in air.
The solid palladium gate has subsequently been replaced by an ultrathin discontinuous
metal film so that larger, less diffuse, molecules can reach the oxide surface and be sensed.
u
Gate voltage, V G
(a)
Figure 8.59 Two types of potentiometric gas microsensors (a) n-channel MISFET and
(b) MISCAP. From Lundstrom et al. (1992)