Page 375 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 375
DEPOSITION OF WAVEGUIDE LAYER 355
Some of the other problems associated with PECVD (TEOS) are that (7) quality
plasma-enhanced chemical vapour-deposited tetraethoxysilane (PETEOS) SiO 2 films are
difficult to achieve at temperatures below 250 °C (Alaonso et al. 1992; Itani and Fukuyama
1997) and (2) TEOS has a low vapour pressure of approximately 2 mTorr (25 °C and
1 atm), which necessitates the heating of all delivery lines and chamber surfaces to
prevent TEOS condensation and prevents gas metering with conventional mass-flow
controllers, thus rendering the resulting process prohibitively expensive (Ballantine et al.
1997). Conventional mass-flow controllers, on the other hand, easily meter silane gas,
but great care must be used because silane is a toxic and pyrophoric gas and constitutes
an explosion hazard at high SiFU concentrations. These limitations add to the cost and
complexity of TEOS and silane-based silicon deposition equipment. To achieve a low
temperature, good quality oxide, and for the circumvention of the safety issues associ-
ated with silane-based oxides and the manufacturing complexities inherent with TEOS,
an alternative precursor needs to be employed.
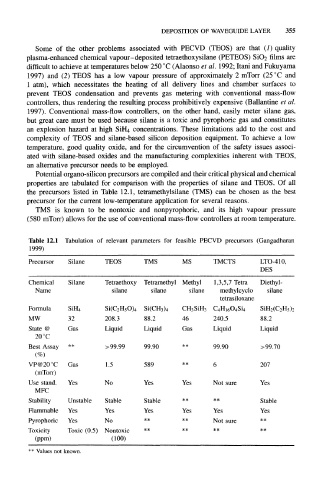
Potential organo-silicon precursors are compiled and their critical physical and chemical
properties are tabulated for comparison with the properties of silane and TEOS. Of all
the precursors listed in Table 12.1, tetramethylsilane (TMS) can be chosen as the best
precursor for the current low-temperature application for several reasons.
TMS is known to be nontoxic and nonpyrophoric, and its high vapour pressure
(580 mTorr) allows for the use of conventional mass-flow controllers at room temperature.
Table 12.1 Tabulation of relevant parameters for feasible PECVD precursors (Gangadharan
1999)
Precursor Silane TEOS TMS MS TMCTS LTO-410,
DBS
Chemical Silane Tetraethoxy Tetramethyl Methyl 1,3,5,7 Tetra Diethyl-
Name silane silane silane methylcyclo silane
tetrasiloxane
Formula SiH 4 Si(C 2H 5O) 4 Si(CH 3) 4 CH 3SiH 3 C 4H 160 4Si 4 SiH 2(C 2H 5) 2
MW 32 208.3 88.2 46 240.5 88.2
State @ Gas Liquid Liquid Gas Liquid Liquid
20 °C
Best Assay ** >99.99 99.90 99.90 > 99.70
VP@20°C Gas 1.5 589 6 207
(mTorr)
Use stand. Yes No Yes Yes Not sure Yes
MFC
Stability Unstable Stable Stable ** ** Stable
Flammable Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Pyrophoric Yes No ** Not sure **
** ** **
Toxicity Toxic (0.5) Nontoxic
(ppm) (100)
** Values not known.