Page 83 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 83
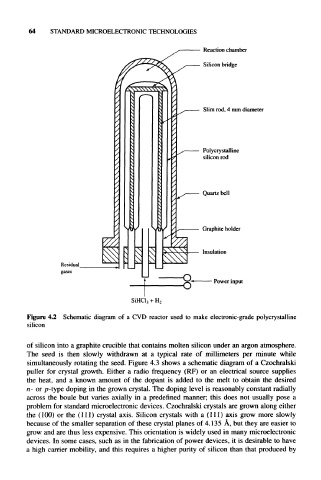
64 STANDARD MICROELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGIES
Reaction chamber
Silicon bridge
Slim rod, 4 mm diameter
Polycrystalline
silicon rod
Quartz bell
Graphite holder
Insulation
Power input
SiHCl 3 + H 2
Figure 4.2 Schematic diagram of a CVD reactor used to make electronic-grade polycrystalline
silicon
of silicon into a graphite crucible that contains molten silicon under an argon atmosphere.
The seed is then slowly withdrawn at a typical rate of millimeters per minute while
simultaneously rotating the seed. Figure 4.3 shows a schematic diagram of a Czochralski
puller for crystal growth. Either a radio frequency (RF) or an electrical source supplies
the heat, and a known amount of the dopant is added to the melt to obtain the desired
n- or P-type doping in the grown crystal. The doping level is reasonably constant radially
across the boule but varies axially in a predefined manner; this does not usually pose a
problem for standard microelectronic devices. Czochralski crystals are grown along either
the (100) or the (111) crystal axis. Silicon crystals with a (111) axis grow more slowly
because of the smaller separation of these crystal planes of 4.135 A, but they are easier to
grow and are thus less expensive. This orientation is widely used in many microelectronic
devices. In some cases, such as in the fabrication of power devices, it is desirable to have
a high carrier mobility, and this requires a higher purity of silicon than that produced by