Page 38 - Modelling in Transport Phenomena A Conceptual Approach
P. 38
2.1. MOLECULAR TRANSPORT 19
Experimental measurements made at steady-state indicate that the rate of heat
flow per unit area is proportional to the temperature gradient, i.e.,
6 Transport -
TI - To
-= k
A v Y (2.1-3)
Energy DroDertv Temperature
.. I
flux gradient
The proportionality constant, k, between the energy flux and the temperature
gradient is called thermal conductivity. In SI units, Q is in W( J/s), A in m2,
dT/dx in K/ m, and k in W/( m. K). The thermal conductivity of a material is,
in general, a function of temperature. However, in many engineering applications
the variation is sufficiently small to be neglected. Thermal conductivity values for
various substances are given in Table D.2 in Appendix D.
The microscopic form of a. (2.1-3) is known as Fourier's law of heat conduction
and is given by
(2.1-4)
in which the subscript y indicates the direction of the energy flux. The negative sign
in Eq. (2.1-4) indicates that heat flows in the direction of decreasing temperature.
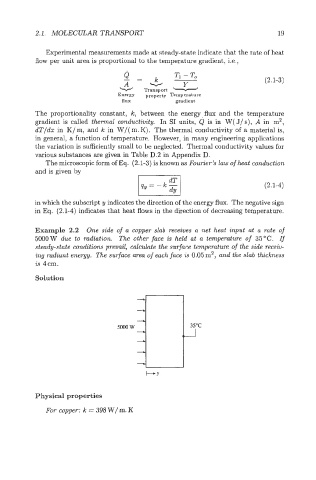
Example 2.2 One side of a wpper slab receives a net heat input at a rate of
5000W due to radiation. The other face is held at a temperature of 35°C. If
steady-state conditions prevail, calculate the surface temperature of the side receiv-
ing radiant energy. The surface area of each face is 0.05m2, and the slab thickness
is 4cm.
Solution
Physical properties
For copper: k = 398 W/ m. K