Page 264 - Modular design for machine tools
P. 264
Engineering Design Fundamentals and Single Flat Joint Characteristics 223
uncertainty in quantitatively determining the magnitude of the flatness
deviation, although the surface roughness can clearly be indicated on the
drawing. This induces another problem—the test specimen with quan-
tified flatness deviation cannot be produced. In consideration of such
unfavorable influences of the flatness deviation on the joint stiffness, they
reported the value b* for the single flat joint under higher normal load-
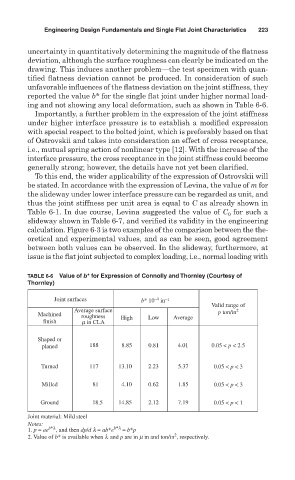
ing and not showing any local deformation, such as shown in Table 6-6.
Importantly, a further problem in the expression of the joint stiffness
under higher interface pressure is to establish a modified expression
with special respect to the bolted joint, which is preferably based on that
of Ostrovskii and takes into consideration an effect of cross receptance,
i.e., mutual spring action of nonlinear type [12]. With the increase of the
interface pressure, the cross receptance in the joint stiffness could become
generally strong; however, the details have not yet been clarified.
To this end, the wider applicability of the expression of Ostrovskii will
be stated. In accordance with the expression of Levina, the value of m for
the slideway under lower interface pressure can be regarded as unit, and
thus the joint stiffness per unit area is equal to C as already shown in
for such a
Table 6-1. In due course, Levina suggested the value of C 0
slideway shown in Table 6-7, and verified its validity in the engineering
calculation. Figure 6-3 is two examples of the comparison between the the-
oretical and experimental values, and as can be seen, good agreement
between both values can be observed. In the slideway, furthermore, at
issue is the flat joint subjected to complex loading, i.e., normal loading with
TABLE 6-6 Value of b* for Expression of Connolly and Thornley (Courtesy of
Thornley)
Joint surfaces b* 10 in –1
–4
Valid range of
Average surface p ton/in 2
Machined roughness High Low Average
finish m in CLA
Shaped or
planed 188 8.85 0.81 4.01 0.05 < p < 2.5
Turned 117 13.10 2.23 5.37 0.05 < p < 3
Milled 81 4.10 0.62 1.85 0.05 < p < 3
Ground 18.5 14.85 2.12 7.19 0.05 < p < 1
Joint material: Mild steel
Notes:
1. p = ae b*l , and then dp/d l = ab*e b*l = b*p
2
2. Value of b* is available when l and p are in m in and ton/in , respectively.