Page 270 - Modular design for machine tools
P. 270
Engineering Design Fundamentals and Single Flat Joint Characteristics 229
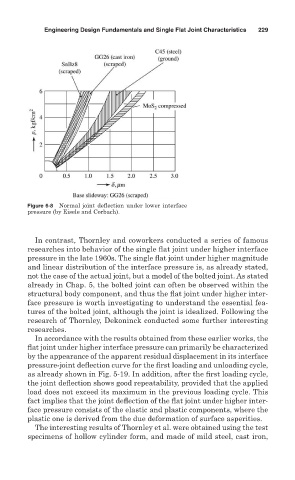
Figure 6-8 Normal joint deflection under lower interface
pressure (by Eisele and Corbach).
In contrast, Thornley and coworkers conducted a series of famous
researches into behavior of the single flat joint under higher interface
pressure in the late 1960s. The single flat joint under higher magnitude
and linear distribution of the interface pressure is, as already stated,
not the case of the actual joint, but a model of the bolted joint. As stated
already in Chap. 5, the bolted joint can often be observed within the
structural body component, and thus the flat joint under higher inter-
face pressure is worth investigating to understand the essential fea-
tures of the bolted joint, although the joint is idealized. Following the
research of Thornley, Dekoninck conducted some further interesting
researches.
In accordance with the results obtained from these earlier works, the
flat joint under higher interface pressure can primarily be characterized
by the appearance of the apparent residual displacement in its interface
pressure-joint deflection curve for the first loading and unloading cycle,
as already shown in Fig. 5-19. In addition, after the first loading cycle,
the joint deflection shows good repeatability, provided that the applied
load does not exceed its maximum in the previous loading cycle. This
fact implies that the joint deflection of the flat joint under higher inter-
face pressure consists of the elastic and plastic components, where the
plastic one is derived from the due deformation of surface asperities.
The interesting results of Thornley et al. were obtained using the test
specimens of hollow cylinder form, and made of mild steel, cast iron,