Page 247 - Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy
P. 247
230 Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy
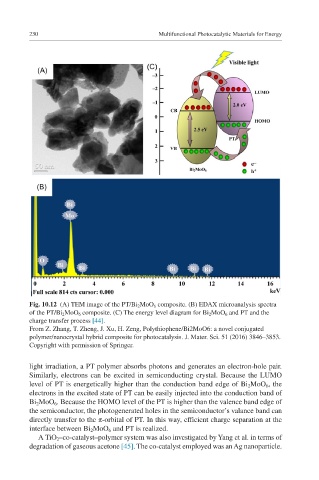
Fig. 10.12 (A) TEM image of the PT/Bi 2 MoO 6 composite. (B) EDAX microanalysis spectra
of the PT/Bi 2 MoO 6 composite. (C) The energy level diagram for Bi 2 MoO 6 and PT and the
charge transfer process [44].
From Z. Zhang, T. Zheng, J. Xu, H. Zeng, Polythiophene/Bi2MoO6: a novel conjugated
polymer/nanocrystal hybrid composite for photocatalysis. J. Mater. Sci. 51 (2016) 3846–3853.
Copyright with permission of Springer.
light irradiation, a PT polymer absorbs photons and generates an electron-hole pair.
Similarly, electrons can be excited in semiconducting crystal. Because the LUMO
level of PT is energetically higher than the conduction band edge of Bi 2 MoO 6 , the
electrons in the excited state of PT can be easily injected into the conduction band of
Bi 2 MoO 6 . Because the HOMO level of the PT is higher than the valence band edge of
the semiconductor, the photogenerated holes in the semiconductor’s valance band can
directly transfer to the π-orbital of PT. In this way, efficient charge separation at the
interface between Bi 2 MoO 6 and PT is realized.
A TiO 2 –co-catalyst–polymer system was also investigated by Yang et al. in terms of
degradation of gaseous acetone [45]. The co-catalyst employed was an Ag nanoparticle.