Page 229 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 229
4.4 NANOCOMPOSITE STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS
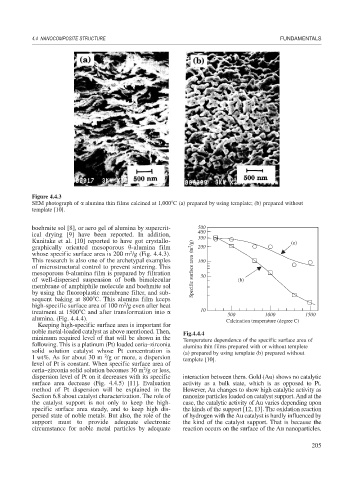
Figure 4.4.3
SEM photograph of alumina thin films calcined at 1,000 C (a) prepared by using template; (b) prepared without
template [10].
boehmite sol [8], or aero gel of alumina by supercrit- 500
400
ical drying [9] have been reported. In addition, 300
Kunitake et al. [10] reported to have got crystallo- (a)
graphically oriented mesoporous -alumina film 200
2
whose specific surface area is 200 m /g (Fig. 4.4.3).
This research is also one of the archetypal examples 100
of microstructural control to prevent sintering. This Specific surface area (m 2 /g)
mesoporous -alumina film is prepared by filtration 50
of well-dispersed suspension of both bimolecular (b)
membrane of amphiphile molecule and boehmite sol
by using the fluoroplastic membrane filter, and sub-
sequent baking at 800 C. This alumina film keeps
2
high-specific surface area of 100 m /g even after heat
treatment at 1500 C and after transformation into 10 500 1000 1500
alumina. (Fig. 4.4.4). Calcination temperature (degree C)
Keeping high-specific surface area is important for
noble metal-loaded catalyst as above mentioned. Then, Fig.4.4.4
minimum required level of that will be shown in the Temperature dependence of the specific surface area of
following. This is a platinum (Pt) loaded ceria–zirconia alumina thin films prepared with or without templete
solid solution catalyst whose Pt concentration is (a) prepared by using template (b) prepared without
2
1 wt%. As for about 30 m /g or more, a dispersion templete [10].
level of Pt is constant. When specific surface area of
2
ceria–zirconia solid solution becomes 30 m /g or less,
dispersion level of Pt on it decreases with its specific interaction between them. Gold (Au) shows no catalytic
surface area decrease (Fig. 4.4.5) [11]. Evaluation activity as a bulk state, which is as opposed to Pt.
method of Pt dispersion will be explained in the However, Au changes to show high catalytic activity as
Section 6.8 about catalyst characterization. The role of nanosize particles loaded on catalyst support. And at the
the catalyst support is not only to keep the high- case, the catalytic activity of Au varies depending upon
specific surface area steady, and to keep high dis- the kinds of the support [12, 13]. The oxidation reaction
persed state of noble metals. But also, the role of the of hydrogen with the Au catalyst is hardly influenced by
support must to provide adequate electronic the kind of the catalyst support. That is because the
circumstance for noble metal particles by adequate reaction occurs on the surface of the Au nanoparticles.
205