Page 562 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 562
APPLICATIONS 27 DEVELOPMENT OF THE THERMORESPONSIVE MAGNETIC NANOPARTICLE
Heating
Magnet
Magnetic
Cooling separation
UCST=20°°C
Dispersion Coagulation Recovery
Cooling 30 sec 5 min
Coagulation
Heating Dispersion
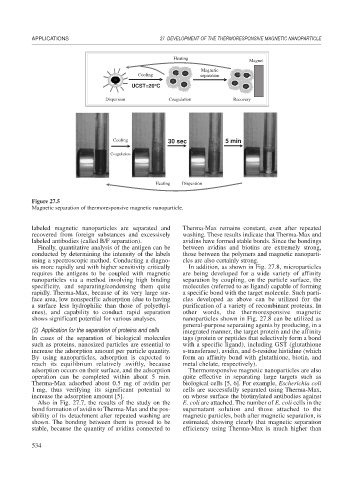
Figure 27.5
Magnetic separation of thermoresponsive magnetic nanoparticle.
labeled magnetic nanoparticles are separated and Therma-Max remains constant, even after repeated
recovered from foreign substances and excessively washing. These results indicate that Therma-Max and
labeled antibodies (called B/F separation). avidins have formed stable bonds. Since the bondings
Finally, quantitative analysis of the antigen can be between avidins and biotins are extremely strong,
conducted by determining the intensity of the labels those between the polymers and magnetic nanoparti-
using a spectroscopic method. Conducting a diagno- cles are also certainly strong.
sis more rapidly and with higher sensitivity critically In addition, as shown in Fig. 27.8, microparticles
requires the antigens to be coupled with magnetic are being developed for a wide variety of affinity
nanoparticles via a method involving high binding separation by coupling, on the particle surface, the
specificity, and separating/condensing them quite molecules (referred to as ligand) capable of forming
rapidly. Therma-Max, because of its very large sur- a specific bond with the target molecule. Such parti-
face area, low nonspecific adsorption (due to having cles developed as above can be utilized for the
a surface less hydrophilic than those of polyethyl- purification of a variety of recombinant proteins. In
enes), and capability to conduct rapid separation other words, the thermoresponsive magnetic
shows significant potential for various analyses. nanoparticles shown in Fig. 27.8 can be utilized as
general-purpose separating agents by producing, in a
(2) Application for the separation of proteins and cells integrated manner, the target protein and the affinity
In cases of the separation of biological molecules tags (protein or peptides that selectively form a bond
such as proteins, nanosized particles are essential to with a specific ligand), including GST (glutathione
increase the adsorption amount per particle quantity. s-transferase), avidin, and 6-residue histidine (which
By using nanoparticles, adsorption is expected to form an affinity bond with glutathione, biotin, and
reach its equilibrium relatively swiftly, because metal chelate, respectively).
adsorption occurs on their surface, and the adsorption Thermoresponsive magnetic nanoparticles are also
operation can be completed within about 5 min. quite effective in separating large targets such as
Therma-Max adsorbed about 0.5 mg of avidin per biological cells [5, 6]. For example, Escherichia coli
1 mg, thus verifying its significant potential to cells are successfully separated using Therma-Max,
increase the adsorption amount [5]. on whose surface the biotinylated antibodies against
Also in Fig. 27.7, the results of the study on the E. coli are attached. The number of E. coli cells in the
bond formation of avidin to Therma-Max and the pos- supernatant solution and those attached to the
sibility of its detachment after repeated washing are magnetic particles, both after magnetic separation, is
shown. The bonding between them is proved to be estimated, showing clearly that magnetic separation
stable, because the quantity of avidins connected to efficiency using Therma-Max is much higher than
534