Page 565 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 565
27 DEVELOPMENT OF THE THERMORESPONSIVE MAGNETIC NANOPARTICLE APPLICATIONS
Anti tag antibody
Cells
Anti-tag-antibody or glutathione
immobilized thermoresponsive
magnetic nanoparticle
Expression of a tagged Glutathione
protein
Cooling and
magnetic
separation
Magnet
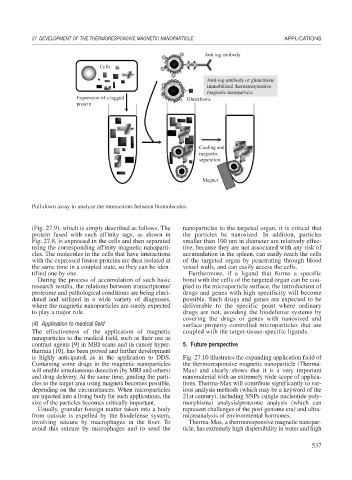
Figure 27.9
Pull-down assay to analyze the interactions between biomolecules.
(Fig. 27.9), which is simply described as follows. The nanoparticles to the targeted organ, it is critical that
protein fused with such affinity tags, as shown in the particles be nanosized. In addition, particles
Fig. 27.8, is expressed in the cells and then separated smaller than 100 nm in diameter are relatively effec-
using the corresponding affinity magnetic nanoparti- tive, because they are not associated with any risk of
cles. The molecules in the cells that have interactions accumulation in the spleen, can easily reach the cells
with the expressed fusion proteins are then isolated at of the targeted organ by penetrating through blood
the same time in a coupled state, so they can be iden- vessel walls, and can easily access the cells.
tified one by one. Furthermore, if a ligand that forms a specific
During the process of accumulation of such basic bond with the cells of the targeted organ can be cou-
research results, the relations between transcriptome/ pled to the microparticle surface, the introduction of
proteome and pathological conditions are being eluci- drugs and genes with high specificity will become
dated and utilized in a wide variety of diagnoses, possible. Such drugs and genes are expected to be
where the magnetic nanoparticles are surely expected deliverable to the specific point where ordinary
to play a major role. drugs are not, avoiding the biodefense systems by
covering the drugs or genes with nanosized and
(4) Application to medical field surface-property-controlled microparticles that are
The effectiveness of the application of magnetic coupled with the target-tissue-specific ligands.
nanoparticles to the medical field, such as their use as
contrast agents [9] in MRI scans and in cancer hyper- 5. Future perspective
thermia [10], has been proved and further development
is highly anticipated, as in the application to DDS. Fig. 27.10 illustrates the expanding application field of
Containing some drugs in the magnetic nanoparticles the thermoresponsive magnetic nanoparticle (Therma-
will enable simultaneous detection (by MRI and others) Max) and clearly shows that it is a very important
and drug delivery. At the same time, guiding the parti- nanomaterial with an extremely wide scope of applica-
cles to the target area using magnets becomes possible, tions. Therma-Max will contribute significantly to var-
depending on the circumstances. When microparticles ious analysis methods (which may be a keyword of the
are injected into a living body for such applications, the 21st century), including SNPs (single nucleotide poly-
size of the particles becomes critically important. morphisms) analysis/proteome analysis (which can
Usually, granular foreign matter taken into a body represent challenges of the post-genome era) and ultra-
from outside is expelled by the biodefense system, microanalysis of environmental hormones.
involving seizure by macrophages in the liver. To Therma-Max, a thermoresponsive magnetic nanopar-
avoid this seizure by microphages and to send the ticle, has extremely high dispersibility in water and high
537