Page 572 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 572
APPLICATIONS 29 DELIVERY TO THE BRAIN
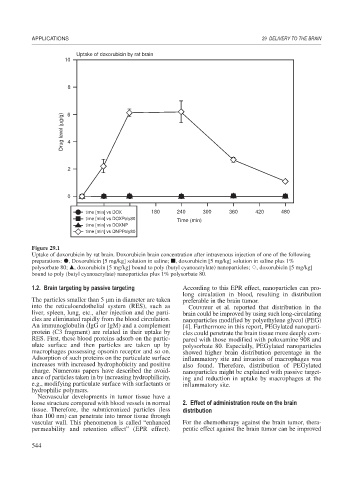
Uptake of doxorubicin by rat brain
10
8
Drug level (μg/g) 6
4
2
0
time [min] vs DOX 180 240 300 360 420 480
time [min] vs DOXPoly80 Time (min)
time [min] vs DOXNP
time [min] vs DNPPoly80
Figure 29.1
Uptake of doxorubicin by rat brain. Doxorubicin brain concentration after intravenous injection of one of the following
preparations: , Doxorubicin [5 mg/kg] solution in saline; , doxorubicin [5 mg/kg] solution in saline plus 1%
polysorbate 80; , doxorubicin [5 mg/kg] bound to poly (butyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles; , doxorubicin [5 mg/kg]
bound to poly (butyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles plus 1% polysorbate 80.
1.2. Brain targeting by passive targeting According to this EPR effect, nanoparticles can pro-
long circulation in blood, resulting in distribution
The particles smaller than 5 m in diameter are taken preferable in the brain tumor.
into the reticuloendothelial system (RES), such as Couvreur et al. reported that distribution in the
liver, spleen, lung, etc., after injection and the parti- brain could be improved by using such long-circulating
cles are eliminated rapidly from the blood circulation. nanoparticles modified by polyethylene glycol (PEG)
An immunoglobulin (IgG or IgM) and a complement [4]. Furthermore in this report, PEGylated nanoparti-
protein (C3 fragment) are related in their uptake by cles could penetrate the brain tissue more deeply com-
RES. First, these blood proteins adsorb on the partic- pared with those modified with poloxamine 908 and
ulate surface and then particles are taken up by polysorbate 80. Especially, PEGylated nanoparticles
macrophages possessing opsonin receptor and so on. showed higher brain distribution percentage in the
Adsorption of such proteins on the particulate surface inflammatory site and invasion of macrophages was
increases with increased hydrophobicity and positive also found. Therefore, distribution of PEGylated
charge. Numerous papers have described the avoid- nanoparticles might be explained with passive target-
ance of particles taken in by increasing hydrophilicity, ing and reduction in uptake by macrophages at the
e.g., modifying particulate surface with surfactants or inflammatory site.
hydrophilic polymers.
Neovascular developments in tumor tissue have a
loose structure compared with blood vessels in normal 2. Effect of administration route on the brain
tissue. Therefore, the submicronized particles (less distribution
than 100 nm) can penetrate into tumor tissue through
vascular wall. This phenomenon is called “enhanced For the chemotherapy against the brain tumor, thera-
permeability and retention effect” (EPR effect). peutic effect against the brain tumor can be improved
544