Page 123 - Neural Network Modeling and Identification of Dynamical Systems
P. 123
112 3. NEURAL NETWORK BLACK BOX APPROACH TO THE MODELING AND CONTROL OF DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS
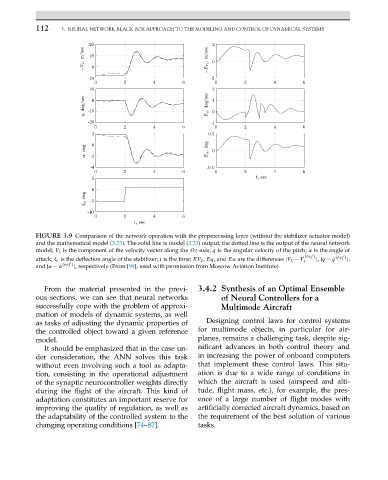
FIGURE 3.9 Comparison of the network operation with the preprocessing layer (without the stabilizer actuator model)
and the mathematical model (3.23). The solid line is model (3.23) output; the dotted line is the output of the neural network
model; V z is the component of the velocity vector along the Oz-axis; q is the angular velocity of the pitch; α is the angle of
(ref ) (ref )
attack; δ e is the deflection angle of the stabilizer; t is the time; EV z , Eq,and Eα are the differences |V z − V z |, |q − q |,
and |α − α (ref ) |, respectively (From [99], used with permission from Moscow Aviation Institute).
From the material presented in the previ- 3.4.2 Synthesis of an Optimal Ensemble
ous sections, we can see that neural networks of Neural Controllers for a
successfully cope with the problem of approxi- Multimode Aircraft
mation of models of dynamic systems, as well
as tasks of adjusting the dynamic properties of Designing control laws for control systems
the controlled object toward a given reference for multimode objects, in particular for air-
model. planes, remains a challenging task, despite sig-
It should be emphasized that in the case un- nificant advances in both control theory and
der consideration, the ANN solves this task in increasing the power of onboard computers
without even involving such a tool as adapta- that implement these control laws. This situ-
tion, consisting in the operational adjustment ation is due to a wide range of conditions in
of the synaptic neurocontroller weights directly which the aircraft is used (airspeed and alti-
during the flight of the aircraft. This kind of tude, flight mass, etc.), for example, the pres-
adaptation constitutes an important reserve for ence of a large number of flight modes with
improving the quality of regulation, as well as artificially corrected aircraft dynamics, based on
the adaptability of the controlled system to the the requirement of the best solution of various
changing operating conditions [74–82]. tasks.