Page 122 - Neural Network Modeling and Identification of Dynamical Systems
P. 122
3.4 ANN-BASED CONTROL OF DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS 111
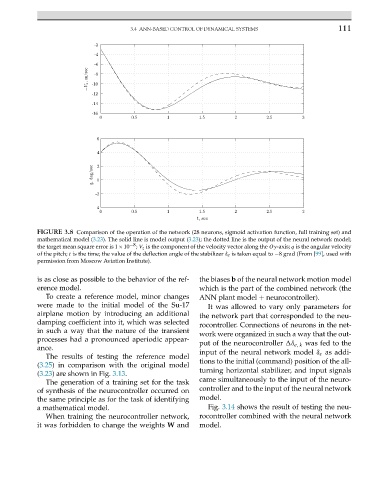
FIGURE 3.8 Comparison of the operation of the network (28 neurons, sigmoid activation function, full training set) and
mathematical model (3.23). The solid line is model output (3.23); the dotted line is the output of the neural network model;
the target mean square error is 1×10 −8 ; V z is the component of the velocity vector along the Oy-axis; q is the angular velocity
of the pitch; t is the time; the value of the deflection angle of the stabilizer δ e is taken equal to −8 grad (From [99], used with
permission from Moscow Aviation Institute).
is as close as possible to the behavior of the ref- the biases b of the neural network motion model
erence model. which is the part of the combined network (the
To create a reference model, minor changes ANN plant model + neurocontroller).
were made to the initial model of the Su-17 It was allowed to vary only parameters for
airplane motion by introducing an additional the network part that corresponded to the neu-
damping coefficient into it, which was selected
rocontroller. Connections of neurons in the net-
in such a way that the nature of the transient
work were organized in such a way that the out-
processes had a pronounced aperiodic appear- put of the neurocontroller δ e, k was fed to the
ance. input of the neural network model δ e as addi-
The results of testing the reference model
(3.25) in comparison with the original model tions to the initial (command) position of the all-
turning horizontal stabilizer, and input signals
(3.23)are showninFig. 3.13.
came simultaneously to the input of the neuro-
The generation of a training set for the task
of synthesis of the neurocontroller occurred on controller and to the input of the neural network
the same principle as for the task of identifying model.
a mathematical model. Fig. 3.14 shows the result of testing the neu-
When training the neurocontroller network, rocontroller combined with the neural network
it was forbidden to change the weights W and model.