Page 121 - Neural Network Modeling and Identification of Dynamical Systems
P. 121
110 3. NEURAL NETWORK BLACK BOX APPROACH TO THE MODELING AND CONTROL OF DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS
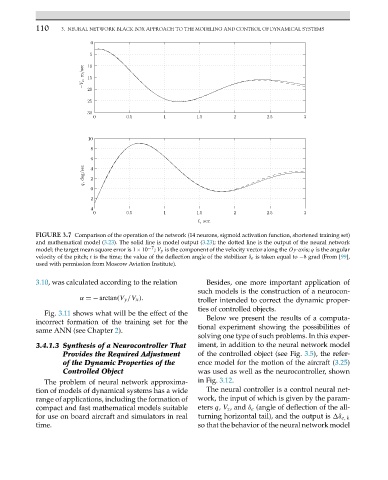
FIGURE 3.7 Comparison of the operation of the network (14 neurons, sigmoid activation function, shortened training set)
and mathematical model (3.23). The solid line is model output (3.23); the dotted line is the output of the neural network
model; the target mean square error is 1 × 10 −7 ; V y is the component of the velocity vector along the Oy-axis; q is the angular
velocity of the pitch; t is the time; the value of the deflection angle of the stabilizer δ e is taken equal to −8 grad (From [99],
used with permission from Moscow Aviation Institute).
3.10, was calculated according to the relation Besides, one more important application of
such models is the construction of a neurocon-
α =−arctan(V y /V x ). troller intended to correct the dynamic proper-
ties of controlled objects.
Fig. 3.11 shows what will be the effect of the
incorrect formation of the training set for the Below we present the results of a computa-
same ANN (see Chapter 2). tional experiment showing the possibilities of
solving one type of such problems. In this exper-
3.4.1.3 Synthesis of a Neurocontroller That iment, in addition to the neural network model
Provides the Required Adjustment of the controlled object (see Fig. 3.5), the refer-
of the Dynamic Properties of the ence model for the motion of the aircraft (3.25)
Controlled Object was used as well as the neurocontroller, shown
The problem of neural network approxima- in Fig. 3.12.
tion of models of dynamical systems has a wide The neural controller is a control neural net-
range of applications, including the formation of work, the input of which is given by the param-
compact and fast mathematical models suitable eters q, V z ,and δ e (angle of deflection of the all-
for use on board aircraft and simulators in real turning horizontal tail), and the output is δ e, k
time. so that the behavior of the neural network model