Page 85 - Offshore Electrical Engineering Manual
P. 85
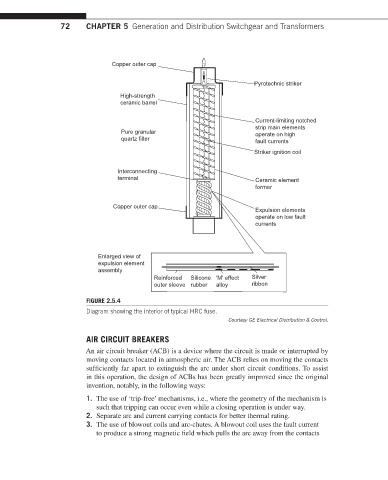
72 CHAPTER 5 Generation and Distribution Switchgear and Transformers
Copper outer cap
Pyrotechnic striker
High-strength
ceramic barrel
Current-limiting notched
strip main elements
Pure granular operate on high
quartz filter fault currents
Striker ignition coil
Interconnecting
terminal Ceramic element
former
Copper outer cap
Expulsion elements
operate on low fault
currents
Enlarged view of
expulsion element
assembly
Reinforced Silicone ‘M’ effect Silver
outer sleeve rubber alloy ribbon
FIGURE 2.5.4
Diagram showing the interior of typical HRC fuse.
Courtesy GE Electrical Distribution & Control.
AIR CIRCUIT BREAKERS
An air circuit breaker (ACB) is a device where the circuit is made or interrupted by
moving contacts located in atmospheric air. The ACB relies on moving the contacts
sufficiently far apart to extinguish the arc under short circuit conditions. To assist
in this operation, the design of ACBs has been greatly improved since the original
invention, notably, in the following ways:
1. The use of ‘trip-free’ mechanisms, i.e., where the geometry of the mechanism is
such that tripping can occur even while a closing operation is under way.
2. Separate arc and current carrying contacts for better thermal rating.
3. The use of blowout coils and arc-chutes. A blowout coil uses the fault current
to produce a strong magnetic field which pulls the arc away from the contacts