Page 71 - Optofluidics Fundamentals, Devices, and Applications
P. 71
52 Cha pte r T h ree
dye is pumped optically by an external laser source. The microchan-
nel terminates at both ends with T-junctions coated with thin layers
of gold or silver to act as mirrors for the optical cavity (Fig. 3-12).
Lasing Characteristics
Lasing was demonstrated with 2-mM rhodamine 640 perchlorate in
methanol as the core stream, and pure methanol as the cladding
stream. A 532-nm pump laser beam (frequency doubled Nd:YAG, 50-Hz
repetition rate, 16-ns pulse) is elongated and focused onto the micro-
channel with a cylindrical lens. A high rate of flow (~ 30 mL/h) is
applied to ensure a rapid replenishment of the dye. Coupled with the
short (16 ns) pulse length, potential photobleaching of the dyes is
avoided at the power levels used (up to 0.15 mJ/pulse).
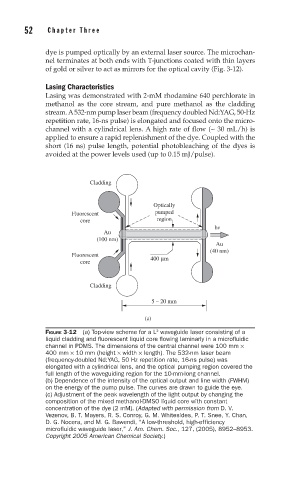
Cladding
Optically
Fluorescent pumped
core region
hv
Au
(100 nm)
Au
(40 nm)
Fluorescent
core 400 μm
Cladding
5 – 20 mm
(a)
2
FIGURE 3-12 (a) Top-view scheme for a L waveguide laser consisting of a
liquid cladding and fl uorescent liquid core fl owing laminarly in a microfl uidic
channel in PDMS. The dimensions of the central channel were 100 mm ×
400 mm × 10 mm (height × width × length). The 532-nm laser beam
(frequency-doubled Nd:YAG, 50 Hz repetition rate, 16-ns pulse) was
elongated with a cylindrical lens, and the optical pumping region covered the
full length of the waveguiding region for the 10-mm-long channel.
(b) Dependence of the intensity of the optical output and line width (FWHM)
on the energy of the pump pulse. The curves are drawn to guide the eye.
(c) Adjustment of the peak wavelength of the light output by changing the
composition of the mixed methanol-DMSO liquid core with constant
concentration of the dye (2 mM). (Adapted with permission from D. V.
Vezenov, B. T. Mayers, R. S. Conroy, G. M. Whitesides, P. T. Snee, Y. Chan,
D. G. Nocera, and M. G. Bawendi, “A low-threshold, high-efficiency
microfluidic waveguide laser,” J. Am. Chem. Soc., 127, (2005), 8952–8953.
Copyright 2005 American Chemical Society.)