Page 65 - Organic Electronics in Sensors and Biotechnology
P. 65
42 Chapter One
~ 30%
–200.0n –200.0n decrease
Drain current (A) –150.0n Drain current (A) –100.0n
–150.0n
–100.0n
–50.0n
Pure P3HT
vanillin vapor
no analyte present –50.0n Pure P3HT &
0.0 0.0
0 20 40 60 80 100 0 20 40 60 80 100
Time (s) Time (s)
–12.0n
–10.0n ~ 72%
Drain current (A) –8.0n decrease
–6.0n
–4.0n
P3HT + Circle K
–2.0n
& vanillin vapor
0.0
0 20 40 60 80 100
Time (s)
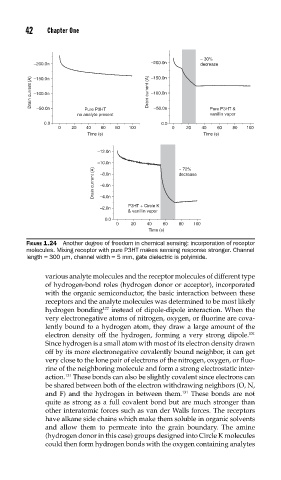
FIGURE 1.24 Another degree of freedom in chemical sensing: incorporation of receptor
molecules. Mixing receptor with pure P3HT makes sensing response stronger. Channel
length = 300 μm, channel width = 5 mm, gate dielectric is polyimide.
various analyte molecules and the receptor molecules of different type
of hydrogen-bond roles (hydrogen donor or acceptor), incorporated
with the organic semiconductor, the basic interaction between these
receptors and the analyte molecules was determined to be most likely
122
hydrogen bonding instead of dipole-dipole interaction. When the
very electronegative atoms of nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine are cova-
lently bound to a hydrogen atom, they draw a large amount of the
electron density off the hydrogen, forming a very strong dipole. 131
Since hydrogen is a small atom with most of its electron density drawn
off by its more electronegative covalently bound neighbor, it can get
very close to the lone pair of electrons of the nitrogen, oxygen, or fluo-
rine of the neighboring molecule and form a strong electrostatic inter-
action. These bonds can also be slightly covalent since electrons can
131
be shared between both of the electron withdrawing neighbors (O, N,
and F) and the hydrogen in between them. These bonds are not
131
quite as strong as a full covalent bond but are much stronger than
other interatomic forces such as van der Walls forces. The receptors
have alkane side chains which make them soluble in organic solvents
and allow them to permeate into the grain boundary. The amine
(hydrogen donor in this case) groups designed into Circle K molecules
could then form hydrogen bonds with the oxygen containing analytes