Page 64 - Organic Electronics in Sensors and Biotechnology
P. 64
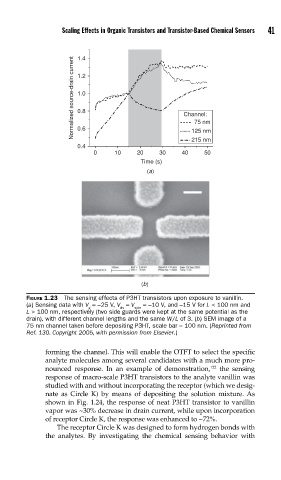
Scaling Effects in Organic Transistors and Transistor-Based Chemical Sensors 41
1.4
Normalized source-drain current 1.2 Channel:
1.0
0.8
75 nm
0.6
215 nm
0.4 125 nm
0 10 20 30 40 50
Time (s)
(a)
(b)
FIGURE 1.23 The sensing effects of P3HT transistors upon exposure to vanillin.
(a) Sensing data with V =−25 V, V = V =−10 V, and −15 V for L < 100 nm and
g ds side
L > 100 nm, respectively (two side guards were kept at the same potential as the
drain), with different channel lengths and the same W/L of 3. (b) SEM image of a
75 nm channel taken before depositing P3HT, scale bar = 100 nm. (Reprinted from
Ref. 130. Copyright 2005, with permission from Elsevier.)
forming the channel. This will enable the OTFT to select the specific
analyte molecules among several candidates with a much more pro-
122
nounced response. In an example of demonstration, the sensing
response of macro-scale P3HT transistors to the analyte vanillin was
studied with and without incorporating the receptor (which we desig-
nate as Circle K) by means of depositing the solution mixture. As
shown in Fig. 1.24, the response of neat P3HT transistor to vanillin
vapor was ~30% decrease in drain current, while upon incorporation
of receptor Circle K, the response was enhanced to ~72%.
The receptor Circle K was designed to form hydrogen bonds with
the analytes. By investigating the chemical sensing behavior with