Page 139 - Photodetection and Measurement - Maximizing Performance in Optical Systems
P. 139
Useful Electronic Circuits and Construction Techniques to Get You Going
132 Chapter Six
The 555 oscillator can achieve a temperature drift of less than 150ppm/°C,
although typical capacitors will drift faster and degrade this figure. We saw in
Chap. 5, however, that it is often helpful to be able to define the source modu-
lation frequency with better precision than this. For example, to avoid the har-
monics of fluorescent light interference we might want to set the frequency
carefully between 4000Hz and 4050Hz and have it stay there with tempera-
ture changes. Or we might want two oscillators with very similar frequencies
to operate a reference-free synchronous detection configuration. Even in
noncritical applications, it is useful to know precisely what the modulation fre-
quency is. In all these cases it will be easier to use a precision resonator oscil-
lator, rather than an RC-oscillator design.
The cheapest route to initial frequency accuracy and temperature stability
(typically ±20ppm/°C) is the 32.768-kHz crystal used in most clocks and
watches. These are available in several through-hole and surface-mount pack-
ages, including tiny 2mm ¥ 7mm long cylinders. The most common way to
excite all resonators is to connect them as a feedback element around a digital
logic gate. Almost any inverting gate will do. This is the internal design of the
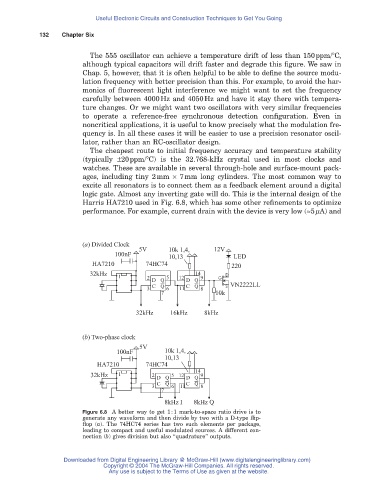
Harris HA7210 used in Fig. 6.8, which has some other refinements to optimize
performance. For example, current drain with the device is very low (ª5mA) and
(a) Divided Clock
5V 10k 1,4, 12V
100nF
10,13 LED
HA7210 74HC74 220
32kHz 14 D
1 2 5 12 9 G
D Q D Q
C Q C Q S VN2222LL
3 6 11 8
7 10k
32kHz 16kHz 8kHz
(b) Two-phase clock
5V
100nF 10k 1,4,
10,13
HA7210 74HC74
14
32kHz 1 2 5 12 9
D Q D Q
C Q C Q
3 6 11 8
7
8kHz I 8kHz Q
Figure 6.8 A better way to get 1:1 mark-to-space ratio drive is to
generate any waveform and then divide by two with a D-type flip-
flop (a). The 74HC74 series has two such elements per package,
leading to compact and useful modulated sources. A different con-
nection (b) gives division but also “quadrature” outputs.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.