Page 77 - Photodetection and Measurement - Maximizing Performance in Optical Systems
P. 77
Fundamental Noise Basics and Calculations
70 Chapter Three
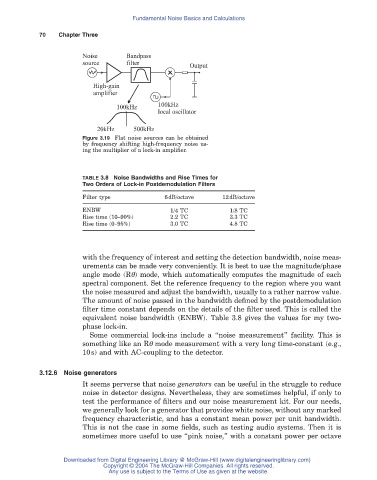
Noise Bandpass
source filter Output
x
High-gain
amplifier
100kHz 100kHz
local oscillator
20kHz 500kHz
Figure 3.19 Flat noise sources can be obtained
by frequency shifting high-frequency noise us-
ing the multiplier of a lock-in amplifier.
TABLE 3.8 Noise Bandwidths and Rise Times for
Two Orders of Lock-in Postdemodulation Filters
Filter type 6dB/octave 12dB/octave
ENBW 1/4 TC 1/8 TC
Rise time (10–90%) 2.2 TC 3.3 TC
Rise time (0–95%) 3.0 TC 4.8 TC
with the frequency of interest and setting the detection bandwidth, noise meas-
urements can be made very conveniently. It is best to use the magnitude/phase
angle mode (Rq) mode, which automatically computes the magnitude of each
spectral component. Set the reference frequency to the region where you want
the noise measured and adjust the bandwidth, usually to a rather narrow value.
The amount of noise passed in the bandwidth defined by the postdemodulation
filter time constant depends on the details of the filter used. This is called the
equivalent noise bandwidth (ENBW). Table 3.8 gives the values for my two-
phase lock-in.
Some commercial lock-ins include a “noise measurement” facility. This is
something like an Rq mode measurement with a very long time-constant (e.g.,
10s) and with AC-coupling to the detector.
3.12.6 Noise generators
It seems perverse that noise generators can be useful in the struggle to reduce
noise in detector designs. Nevertheless, they are sometimes helpful, if only to
test the performance of filters and our noise measurement kit. For our needs,
we generally look for a generator that provides white noise, without any marked
frequency characteristic, and has a constant mean power per unit bandwidth.
This is not the case in some fields, such as testing audio systems. Then it is
sometimes more useful to use “pink noise,” with a constant power per octave
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.