Page 84 - Photodetection and Measurement - Maximizing Performance in Optical Systems
P. 84
Fundamental Noise Basics and Calculations
Fundamental Noise Basics and Calculations 77
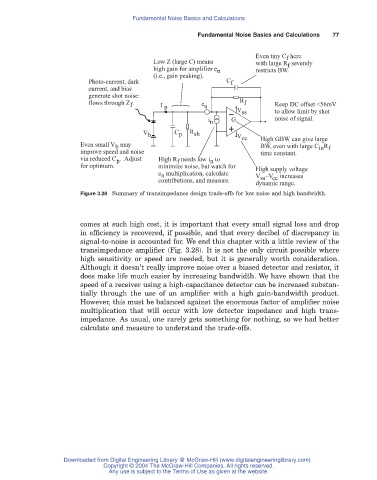
Even tiny C here
f
Low Z (large C) means with large R severely
f
high gain for amplifier e n restricts BW.
(i.e., gain peaking).
Photo-current, dark C f
current, and bias
generate shot noise:
flows through Z . I e } n R f Keep DC offset <56mV
f
p
V ss to allow limit by shot
i n G noise of signal.
V b C p R sh V cc
Even small V may High GBW can give large
BW, even with large C R
b
in f
improve speed and noise time constant.
via reduced C . Adjust High R needs low i to
p
n
f
for optimum. minimize noise, but watch for High supply voltage
e multiplication, calculate V –V increases
n
contributions, and measure. ss cc
dynamic range.
Figure 3.28 Summary of transimpedance design trade-offs for low noise and high bandwidth.
comes at such high cost, it is important that every small signal loss and drop
in efficiency is recovered, if possible, and that every decibel of discrepancy in
signal-to-noise is accounted for. We end this chapter with a little review of the
transimpedance amplifier (Fig. 3.28). It is not the only circuit possible where
high sensitivity or speed are needed, but it is generally worth consideration.
Although it doesn’t really improve noise over a biased detector and resistor, it
does make life much easier by increasing bandwidth. We have shown that the
speed of a receiver using a high-capacitance detector can be increased substan-
tially through the use of an amplifier with a high gain-bandwidth product.
However, this must be balanced against the enormous factor of amplifier noise
multiplication that will occur with low detector impedance and high trans-
impedance. As usual, one rarely gets something for nothing, so we had better
calculate and measure to understand the trade-offs.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.